⭐ 가시다(gasida) 님이 진행하는 KANS(**K**ubernetes **A**dvanced **N**etworking **S**tudy)3기 실습 게시글입니다.
게시글 상 소스코드, 사진에서 ****굵게**** '''코드쉘''' 에 대한 부분이 들어가있을수도 있습니다.
⭐코드에서 실습 시 사용하는 변수가 들어갈 수 있습니다. 아래의 정보를 사용하고있습니다.
#route53 Domain: jjongguet.com
#AWS Secret Key: jjongkey
#Aws .pem Key: jjong-key.pem
실습 환경 구성
구성 : VPC 1개(퍼블릭 서브넷 2개), EC2 인스턴스 3대 (Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, t3.xlarge - vCPU 4 , Mem 16) , testpc 1대는 t3.small
- CloudFormation 스택 실행 시 파라미터를 기입하면, 해당 정보가 반영되어 배포됩니다.
- CloudFormation 에 EC2의 UserData 부분(Script 실행)으로 실습 환경에 필요한 기본 설정들이 자동으로 진행됩니다.
CloudFormation 스택 배포 ← 실행하는 PC에 aws cli 설치되어 있고, aws configure 자격증명 설정 상태
- 설치 옵션 :
kubeadm init ... **--skip-phases=addon/kube-proxy**
# YAML 파일 다운로드
curl -O https://s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/cloudformation.cloudneta.net/kans/**kans-8w.yaml**
# CloudFormation 스택 배포
# aws cloudformation deploy --template-file kans-8w.yaml --stack-name mylab --parameter-overrides KeyName=<My SSH Keyname> SgIngressSshCidr=<My Home Public IP Address>/32 --region ap-northeast-2
예시) aws cloudformation deploy --template-file **kans-8w.yaml** --stack-name **mylab** --parameter-overrides KeyName=jjongkey SgIngressSshCidr=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)/32 --region ap-northeast-2
## Tip. 인스턴스 타입 변경 : MyInstanceType=t3.xlarge (vCPU 4, Mem 16)
예시) aws cloudformation deploy --template-file **kans-8w.yaml** --stack-name **mylab** --parameter-overrides **MyInstanceType=t3.xlarge** KeyName=jjongkey SgIngressSshCidr=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)/32 --region ap-northeast-2
# CloudFormation 스택 배포 완료 후 작업용 EC2 IP 출력
aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name **mylab** --query 'Stacks[*].**Outputs[0]**.OutputValue' --output text --region ap-northeast-2
# [모니터링] CloudFormation 스택 상태 : 생성 완료 확인
**while true; do
date
AWS_PAGER="" aws cloudformation list-stacks \
--stack-status-filter CREATE_IN_PROGRESS CREATE_COMPLETE CREATE_FAILED DELETE_IN_PROGRESS DELETE_FAILED \
--query "StackSummaries[*].{StackName:StackName, StackStatus:StackStatus}" \
--output table
sleep 1
done**
# 배포된 aws ec2 유동 공인 IP 확인
**aws ec2 describe-instances --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIPAdd:PublicIpAddress,InstanceName:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" --filters Name=instance-state-name,Values=running --output text**
# EC2 SSH 접속 : 바로 접속하지 말고, 5~7분 정도 후에 접속 할 것
ssh -i *~/.ssh/jjong-key.pem* **ubuntu**@$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name **mylab** --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text --region ap-northeast-2)
...
*(⎈|kubernetes-admin@kubernetes:N/A) root@k8s-s:~# <- kubeps 가 나오지 않을 경우 ssh logout 후 다시 ssh 접속 할 것!*EC2 생성 수량 부족 실패 시: 사용자 계정의 해당 리전에 EC2 최대 갯수 제한 일 경우, Service Quotas (EC2) 증설 요청으로 해결 - 링크 EC2 요청- Limit Type(EC2 Instances) ⇒ 서울 리전, All Standard (A, C, D, H, I, M, R, T, Z) Instances, New limit value(40 정도)
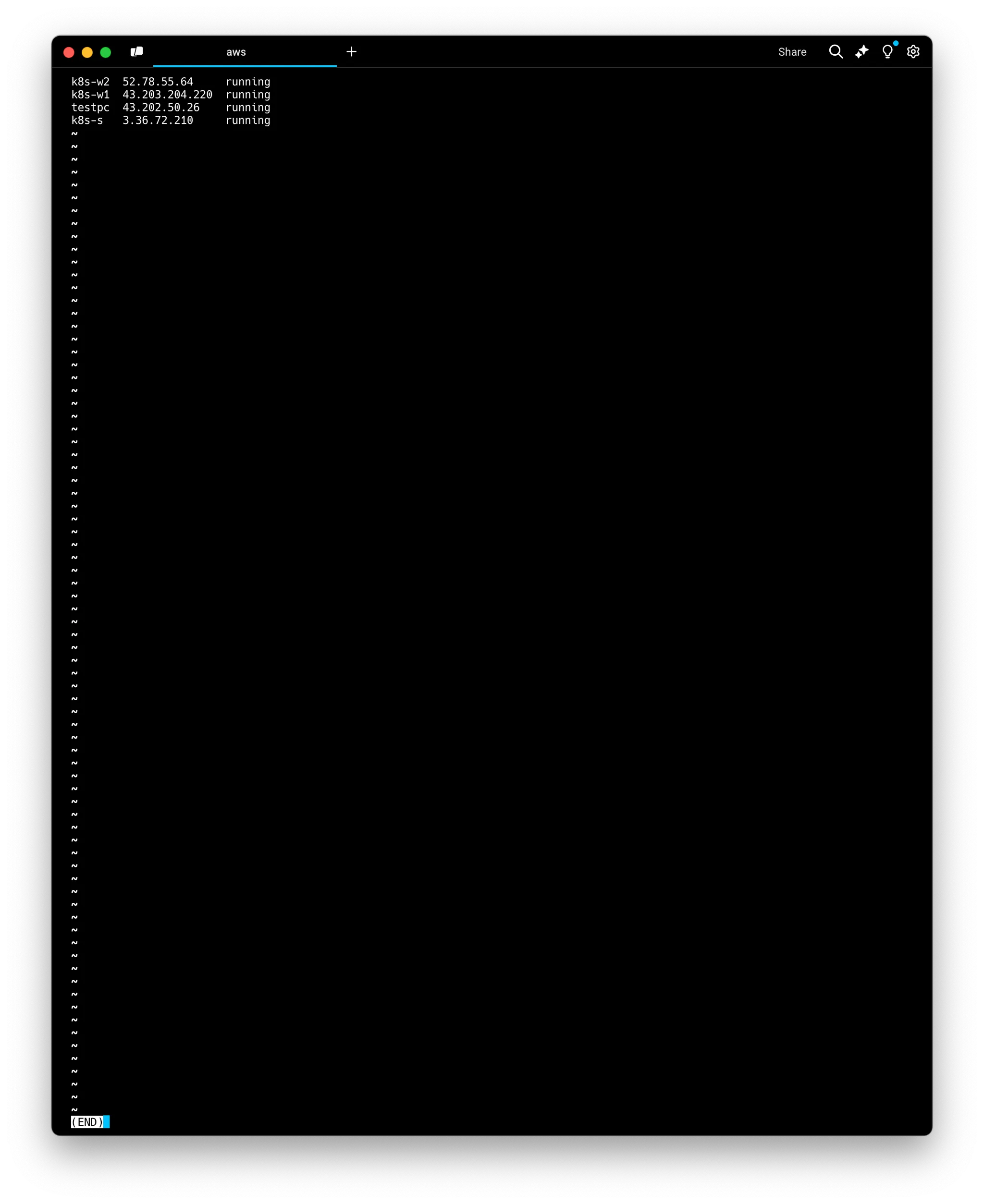
IP정보
1. Cillium?
LInux Network Stack 의 단점
리눅스 네트워크스택은 복잡하게 구성되어있는데
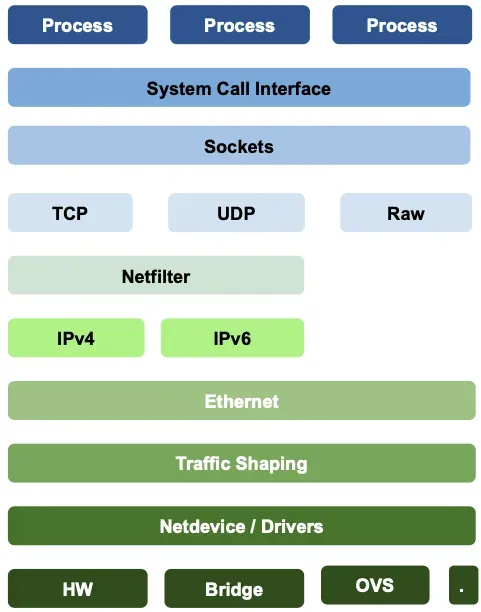
리눅스 네트워크 스택의 단점은 복잡하고, 변경에 시간이 걸리며, 레이어를 건너뛰기 어렵다는점이다.
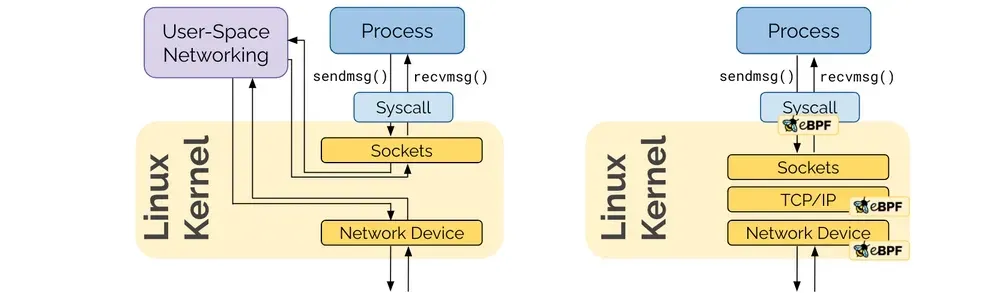
1.1 BPF/eBPF ?
BPF(Barkeley Packet Filter) Kernel hooks: BPF는 커널에 삽입하여 패킷을 필터링 할 수 있으며, 다양한 영역에서 Hook을 통해서 접근가능하다.
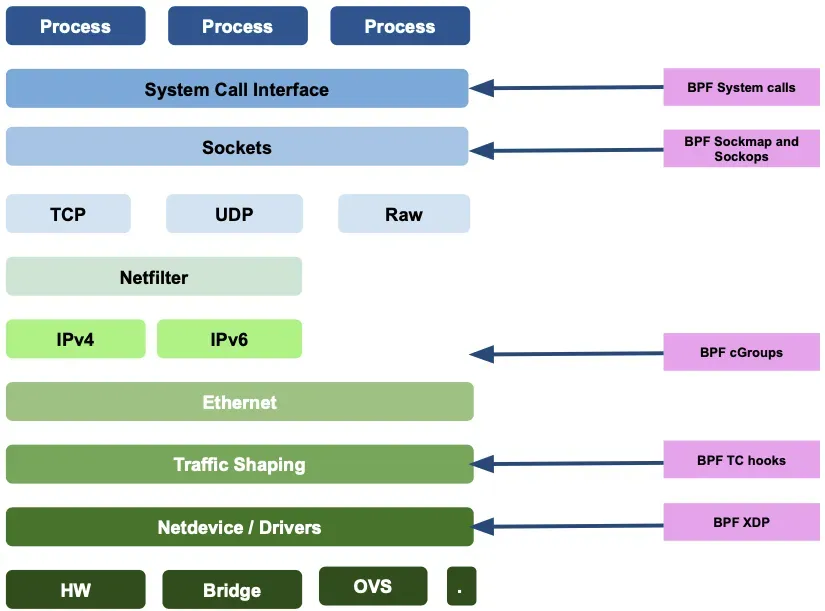
eBPF는 extended BPF 로써, BPF를 다양한 영역(보안,추적,네트워킹, 모니터링) 에서 활용하기 시작했으며
커널 내의 (샌드박스 내에서) 자유롭게 프로그래밍하여 적용 가능합니다.
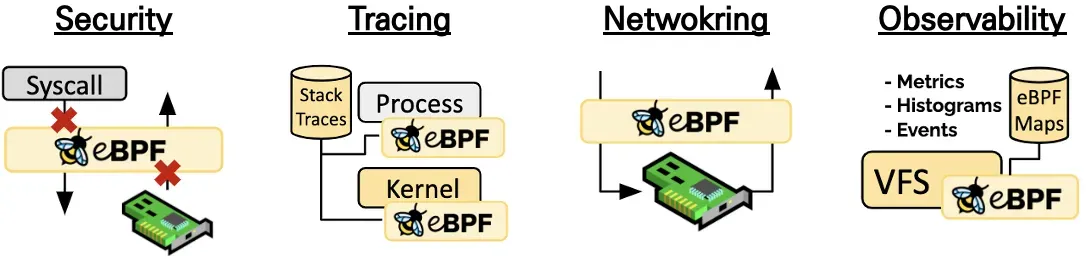
1.2 Cilium
Cilium 은 eBPF 를 기반으로 Pod Network환경+보안을 제공하는 CNI PLUGIN 이며
Linux 컨테이너 관리 플랫폼을 사용하여 배포된 응용 프로그램 서비스 간의 네트워크 및 API 연결을 제공하는 오픈 소스 소프트웨어이다.
추가적인 App이나 설정변경없이 Linux Kenral을 자유롭게 프로그래밍해서 동작가능
모든패킷을 가로채기 위해서 NIC의 ingress TC hooks를 사용하는 특징이 있다.
TC: Kernal 에서 동작하는 패킷 스케쥴러
네트워크 모드: 터널모드(VXLAN, GENEVE), Native 라우팅 모드 를 제공
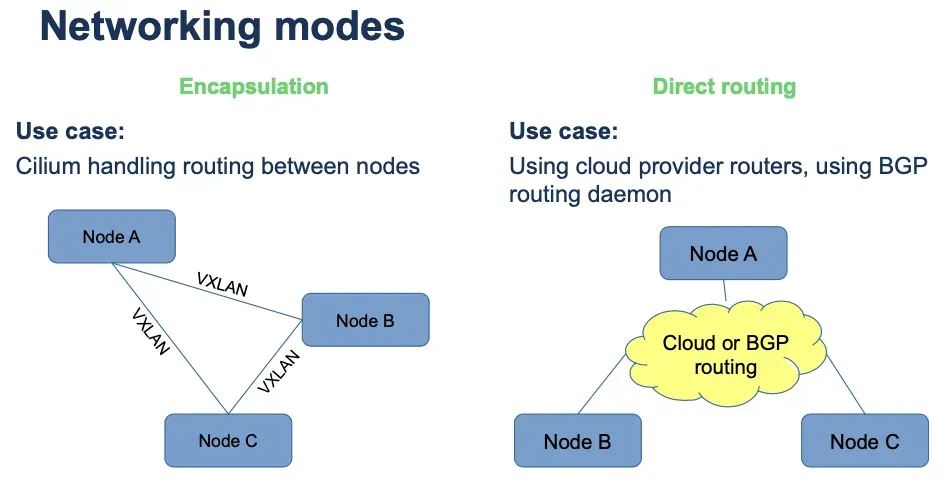
현재 Cilium은 GKE dataplane, EKS Anywhere에서 기본CNI로 사용하고있다.
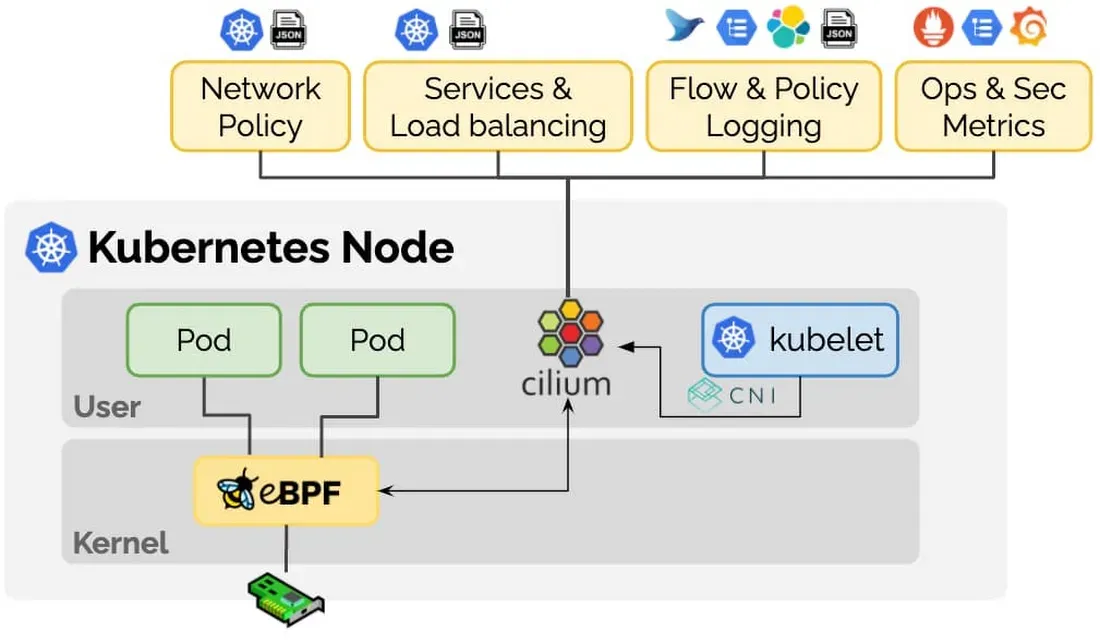
1.3 Cilium 아키텍쳐
구성요소
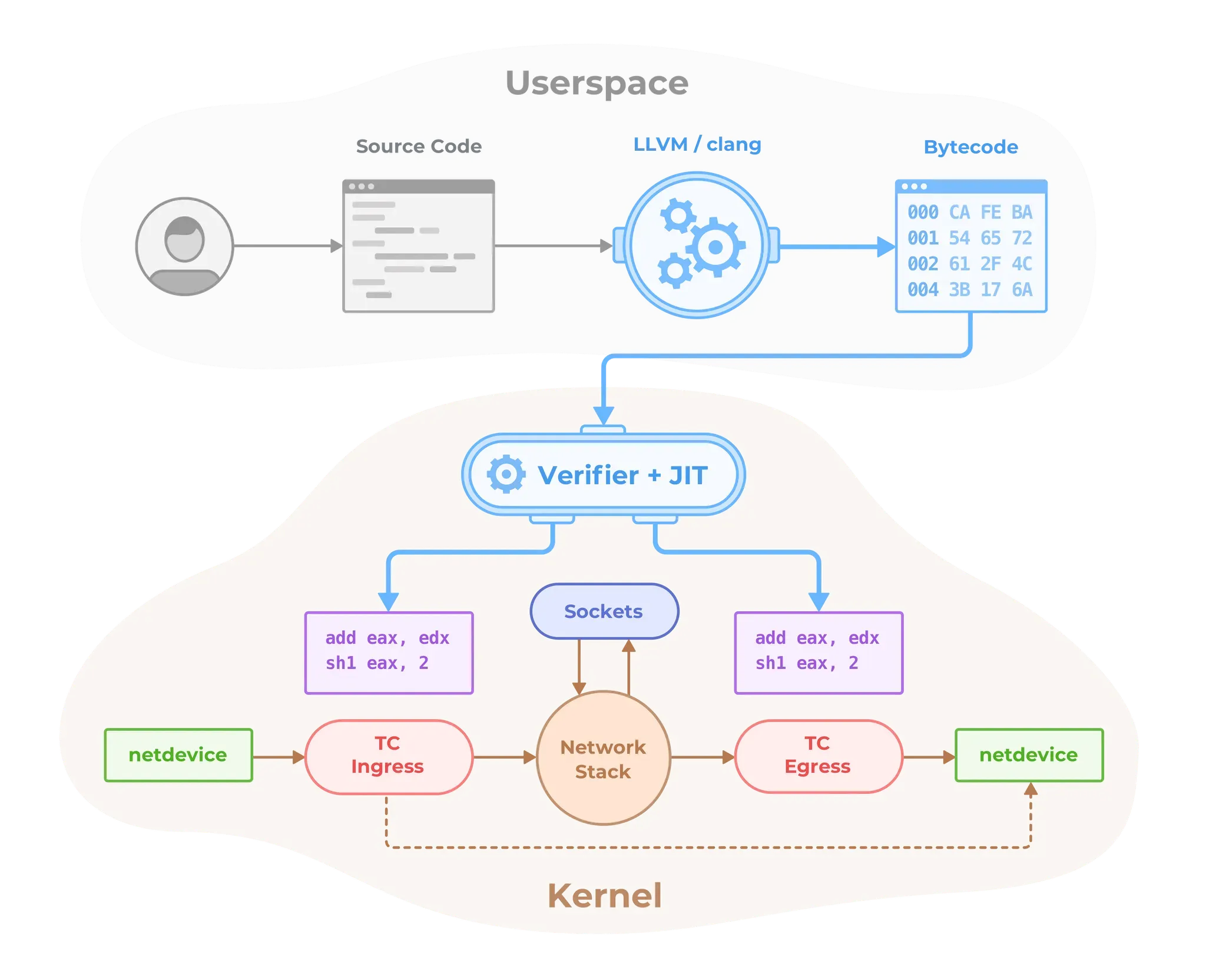
- Cilium Agent : 데몬셋으로 실행, K8S API 설정으로 부터 '네트워크 설정, 네트워크 정책, 서비스 부하분산, 모니터링' 등을 수행하며, eBPF 프로그램을 관리한다.
- Cilium Client (CLI) : Cilium 커멘드툴, eBPF maps 에 직접 접속하여 상태를 확인할 수 있다.
- Cilium Operator : K8S 클러스터에 대한 한 번씩 처리해야 하는 작업을 관리.
- Hubble : 네트워크와 보안 모니터링 플랫폼 역할을 하여, 'Server, Relay, Client, Graphical UI' 로 구성되어 있다.
- Data Store : Cilium Agent 간의 상태를 저장하고 전파하는 데이터 저장소, 2가지 종류 중 선택(K8S CRDs, Key-Value Store)
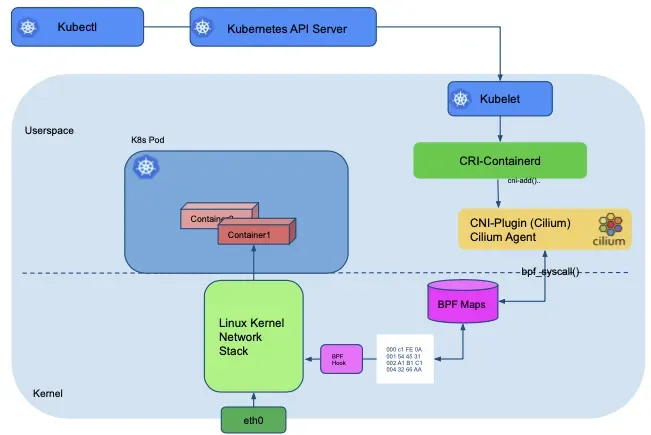
2. Cilium 배포
2.1 배포하기
# 모니터링
watch -d kubectl get node,pod -A -owide
#
helm repo add cilium https://helm.cilium.io/
helm repo update
#
helm install cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.16.3 --namespace kube-system \
--set k8sServiceHost=192.168.10.10 --set k8sServicePort=6443 --set debug.enabled=true \
--set rollOutCiliumPods=true --set routingMode=native --set autoDirectNodeRoutes=true \
--set bpf.masquerade=true --set bpf.hostRouting=true --set endpointRoutes.enabled=true \
--set ipam.mode=kubernetes --set k8s.requireIPv4PodCIDR=true --set kubeProxyReplacement=true \
--set ipv4NativeRoutingCIDR=192.168.0.0/16 --set installNoConntrackIptablesRules=true \
--set hubble.ui.enabled=true --set hubble.relay.enabled=true --set prometheus.enabled=true --set operator.prometheus.enabled=true --set hubble.metrics.enableOpenMetrics=true \
--set hubble.metrics.enabled="{dns:query;ignoreAAAA,drop,tcp,flow,port-distribution,icmp,httpV2:exemplars=true;labelsContext=source_ip\,source_namespace\,source_workload\,destination_ip\,destination_namespace\,destination_workload\,traffic_direction}" \
--set operator.replicas=1
## 주요 파라미터 설명
--set debug.enabled=true # cilium 파드에 로그 레벨을 debug 설정
--set autoDirectNodeRoutes=true # 동일 대역 내의 노드들 끼리는 상대 노드의 podCIDR 대역의 라우팅이 자동으로 설정
--set endpointRoutes.enabled=true # 호스트에 endpoint(파드)별 개별 라우팅 설정
--set hubble.relay.enabled=true --set hubble.ui.enabled=true # hubble 활성화
--set ipam.mode=kubernetes --set k8s.requireIPv4PodCIDR=true # k8s IPAM 활용
--set kubeProxyReplacement=true # kube-proxy 없이 (최대한) 대처할수 있수 있게
--set ipv4NativeRoutingCIDR=192.168.0.0/16 # 해당 대역과 통신 시 IP Masq 하지 않음, 보통 사내망 대역을 지정
--set operator.replicas=1 # cilium-operator 파드 기본 1개
--set enableIPv4Masquerade=true --set bpf.masquerade=true # 파드를 위한 Masquerade , 추가로 Masquerade 을 BPF 로 처리 >> enableIPv4Masquerade=true 인 상태에서 추가로 bpf.masquerade=true 적용이 가능
# 설정 및 확인
ip -c addr
kubectl get node,pod,svc -A -owide
iptables -t nat -S
iptables -t filter -S
iptables -t raw -S
iptables -t mangle -S
conntrack -L
kubectl get crd
kubectl get ciliumnodes # cilium_host 인터페이스의 IP 확인 : CILIUMINTERNALIP
kubectl get ciliumendpoints -A
kubectl get cm -n kube-system cilium-config -o json | jq
kubetail -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium --since 1h
kubetail -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy --since 1h
# Native XDP 지원 NIC 확인 : https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/bpf/progtypes/#xdp-drivers
ethtool -i ens5
driver: ena
version: 6.8.0-1015-aws
...
# https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/operations/performance/tuning/#bypass-iptables-connection-tracking
watch -d kubectl get pod -A # 모니터링
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system --reuse-values --set installNoConntrackIptablesRules=true
# 확인: 기존 raw 에 아래 rule 추가 확인
iptables -t raw -S | grep notrack
-A CILIUM_OUTPUT_raw -d 192.168.0.0/16 -m comment --comment "cilium: NOTRACK for pod traffic" -j CT --notrack
-A CILIUM_OUTPUT_raw -s 192.168.0.0/16 -m comment --comment "cilium: NOTRACK for pod traffic" -j CT --notrack
...
conntrack -F
conntrack -L
conntrack -L |grep -v 2379

Cilium CLI 설치
# Cilium CLI 설치
CILIUM_CLI_VERSION=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium-cli/main/stable.txt)
CLI_ARCH=amd64
if [ "$(uname -m)" = "aarch64" ]; then CLI_ARCH=arm64; fi
curl -L --fail --remote-name-all https://github.com/cilium/cilium-cli/releases/download/${CILIUM_CLI_VERSION}/cilium-linux-${CLI_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
sha256sum --check cilium-linux-${CLI_ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256sum
sudo tar xzvfC cilium-linux-${CLI_ARCH}.tar.gz /usr/local/bin
rm cilium-linux-${CLI_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
# 확인
cilium status --wait
cilium config view
# cilium 데몬셋 파드 내에서 cilium 명령어로 상태 확인
export CILIUMPOD0=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-s -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
alias c0="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD0 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
c0 status --verbose
...
KubeProxyReplacement: True [ens5 192.168.10.10 fe80::57:abff:fee3:da8d (Direct Routing)]
...
IPAM: IPv4: 2/254 allocated from 172.16.0.0/24,
Allocated addresses:
172.16.0.159 (router)
172.16.0.171 (health)
...
Routing: Network: Native Host: BPF
...
Device Mode: veth
Masquerading: BPF [ens5] 192.168.0.0/16 [IPv4: Enabled, IPv6: Disabled]
...
Proxy Status: OK, ip 172.16.0.159, 0 redirects active on ports 10000-20000, Envoy: external
...
KubeProxyReplacement Details:
Status: True
Socket LB: Enabled
Socket LB Tracing: Enabled
Socket LB Coverage: Full
Devices: ens5 192.168.10.10 fe80::57:abff:fee3:da8d (Direct Routing)
Mode: SNAT
Backend Selection: Random
Session Affinity: Enabled
Graceful Termination: Enabled
NAT46/64 Support: Disabled
XDP Acceleration: Disabled
Services:
- ClusterIP: Enabled
- NodePort: Enabled (Range: 30000-32767)
- LoadBalancer: Enabled
- externalIPs: Enabled
- HostPort: Enabled
BPF Maps: dynamic sizing: on (ratio: 0.002500)
...
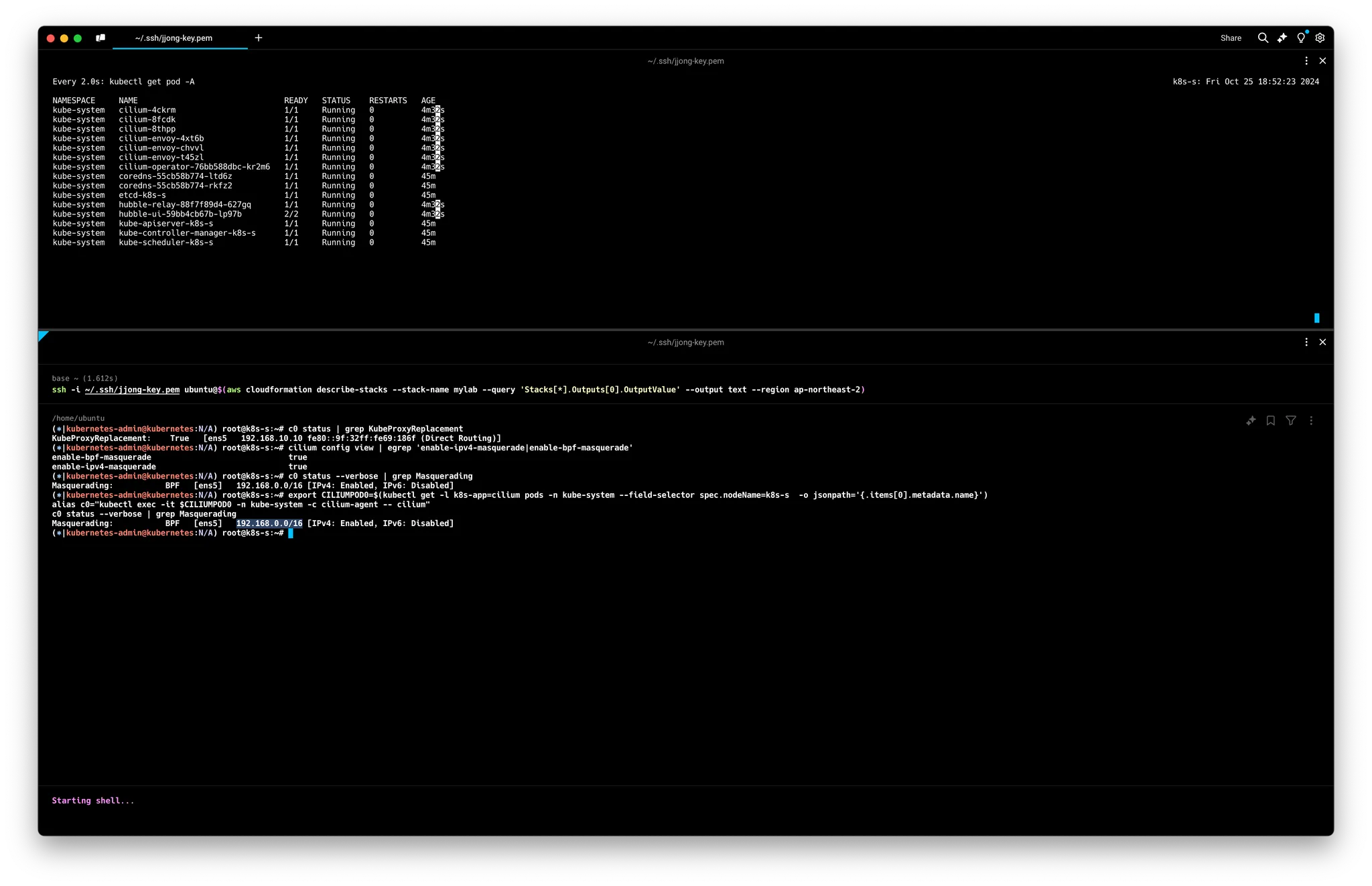
# Native Routing 확인 : # 192.168.0.0/16 대역은 IP Masq 없이 라우팅
c0 status | grep KubeProxyReplacement
ubeProxyReplacement: True [ens5 192.168.10.10 fe80::57:abff:fee3:da8d (Direct Routing)]
# enableIPv4Masquerade=true(기본값) , bpf.masquerade=true 확인
cilium config view | egrep 'enable-ipv4-masquerade|enable-bpf-masquerade'
enable-bpf-masquerade true
enable-ipv4-masquerade true
c0 status --verbose | grep Masquerading
Masquerading: BPF [ens5] 192.168.0.0/16 [IPv4: Enabled, IPv6: Disabled]
# Configure the eBPF-based ip-masq-agent
# https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/concepts/masquerading/
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system --reuse-values --set ipMasqAgent.enabled=true
#
cilium config view | grep -i masq
enable-bpf-masquerade true
enable-ip-masq-agent true
...
export CILIUMPOD0=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-s -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
alias c0="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD0 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
c0 status --verbose | grep Masquerading
Masquerading: BPF (ip-masq-agent) [ens5] 192.168.0.0/16 [IPv4: Enabled, IPv6: Disabled]
kubectl get cm -n kube-system cilium-config -o yaml | grep ip-masq
enable-ip-masq-agent: "true"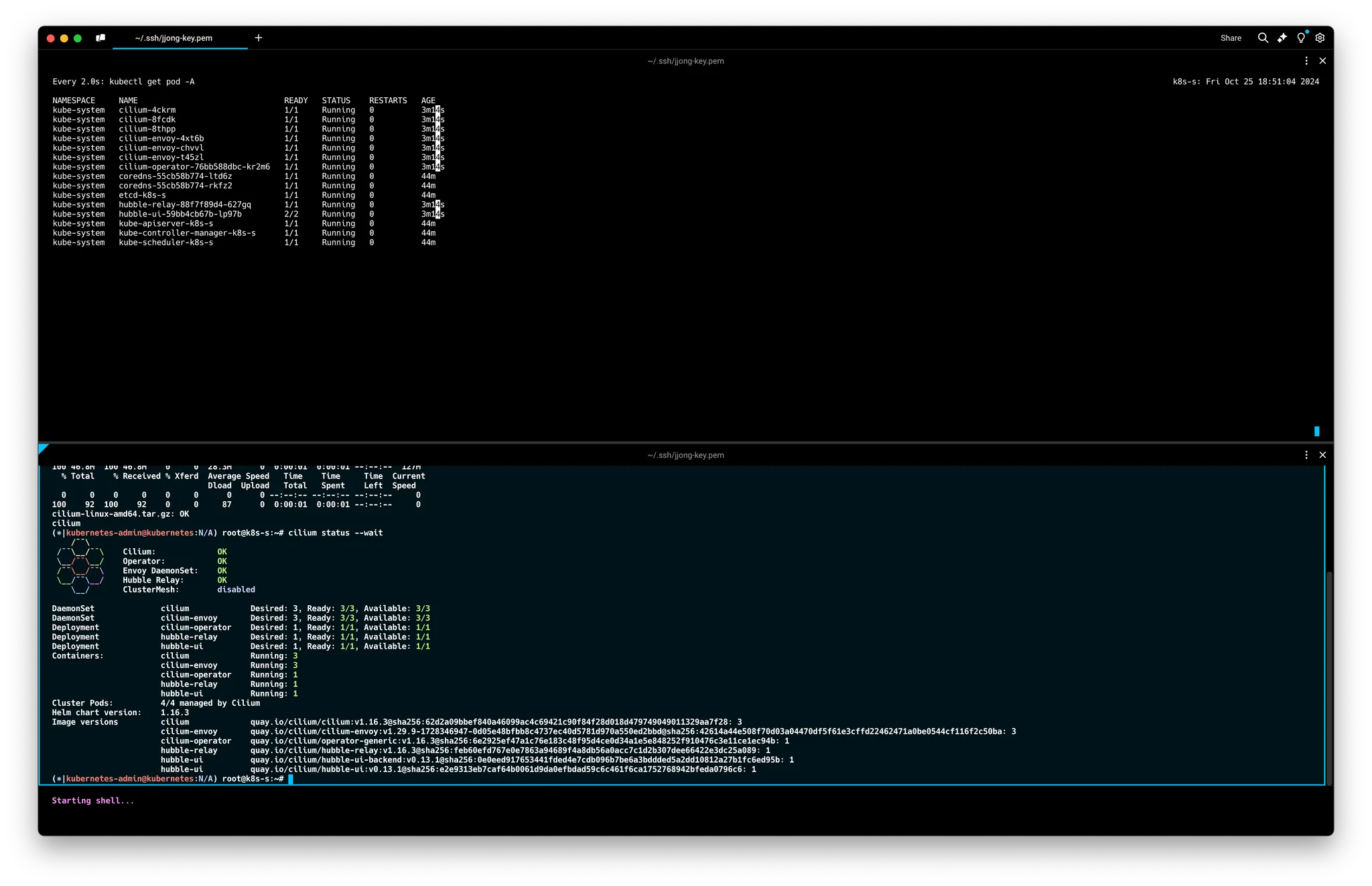
2.2 Cilium 기본 정보 확인
변수& 단축키 확인
# cilium 파드 이름
export CILIUMPOD0=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-s -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
export CILIUMPOD1=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-w1 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
export CILIUMPOD2=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-w2 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
# 단축키(alias) 지정
alias c0="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD0 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
alias c1="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD1 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
alias c2="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD2 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
alias c0bpf="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD0 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- bpftool"
alias c1bpf="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD1 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- bpftool"
alias c2bpf="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD2 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- bpftool"
# Hubble UI 웹 접속
kubectl patch -n kube-system svc hubble-ui -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
HubbleUiNodePort=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system hubble-ui -o jsonpath={.spec.ports[0].nodePort})
echo -e "Hubble UI URL = http://$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip):$HubbleUiNodePort"
# 자주 사용 명령
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system --reuse-values --set
kubetail -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium --since 12h
kubetail -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy --since 12h
자주사용하는 Cilium CLI 명령어
# cilium 파드 확인
kubectl get pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium -owide
# cilium 파드 재시작
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart ds/cilium
혹은
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium
# cilium 설정 정보 확인
cilium config view
# cilium 파드의 cilium 상태 확인
c0 status --verbose
# cilium 엔드포인트 확인
kubectl get ciliumendpoints -A
c0 endpoint list
c0 bpf endpoint list
c0 map get cilium_lxc
c0 ip list
# Manage the IPCache mappings for IP/CIDR <-> Identity
c0 bpf ipcache list
# Service/NAT List 확인
c0 service list
c0 bpf lb list
c0 bpf lb list --revnat
c0 bpf nat list
# List all open BPF maps
c0 map list
c0 map list --verbose
# List contents of a policy BPF map : Dump all policy maps
c0 bpf policy get --all
c0 bpf policy get --all -n
# cilium monitor
c0 monitor -v
c0 monitor -v --type l7네트워크 기본정보 확인: k8s-w1/w2 에 접속 후 ip -c link/route 정보확인
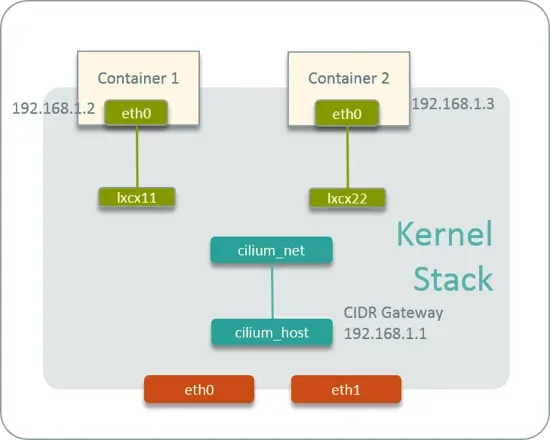
# 네트워크 인터페이스 정보 확인
ip -br -c link
ip -br -c addr
--------------------------------------------
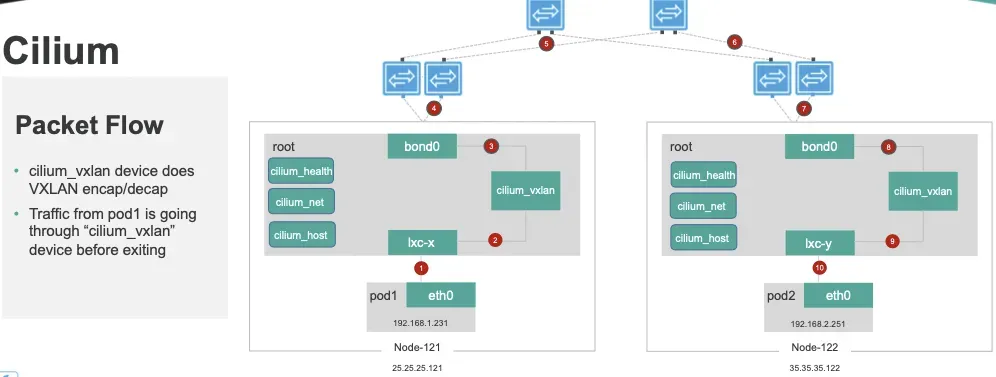
# cilium_net 과 cilium_host 는 veth peer 관계이며, cilium_host 는 파드의 GW IP 주소로 지정되며 32bit 이다
ip -c addr show cilium_net ; ip -c addr show cilium_host
5: cilium_net@cilium_host: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 36:88:bf:c9:5c:6c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
...
6: cilium_host@cilium_net: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 4e:6a:8e:44:85:61 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.16.1.254/32 scope link cilium_host
...
# proxy arp 는 disable(0) 상태이며, 파드와 연결된 lxc 도 모두 0 이다
# 파드의 32bit ip의 gw 가 각각 연결된 veth 인터페이스의 mac 으로 cilium_host 의 IP/MAC 응답을 처리한다, 어떻게 동작이 되는걸까요? >> eBPF program!!!
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/cilium_net/proxy_arp
0
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/cilium_host/proxy_arp
0
# lxc_health 인터페이스는 veth 로 cilium(NET NS 0, 호스트와 다름)과 veth pair 이다 - 링크
# cilium 인터페이스에 파드 IP가 할당되어 있으며, cilium-health-responder 로 동작한다
lsns -t net
2.3 Hubble UI & CLI
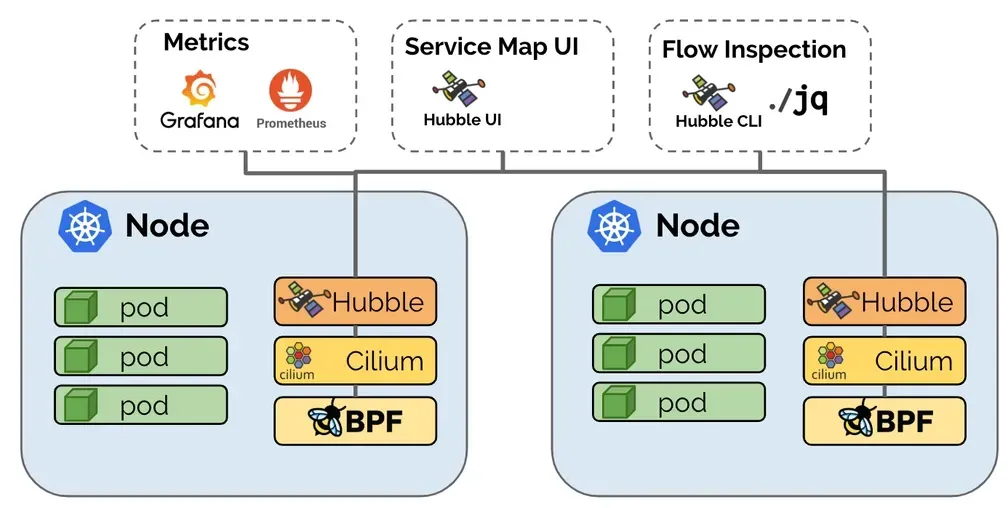
Hubble: 통신 및 서비스와 네트워킹 인프라의 동작에 대한 심층적인 가시성을 완전히 투명한 방식으로 제공하는 관찰성을 제공
- Hubble is a fully distributed networking and security observability platform. → 네트워크/보안 모니터링
- It is built on top of Cilium and eBPF to enable deep visibility into the communication and behavior of services as well as the networking infrastructure in a completely transparent manner. without requiring the application to change in any way. → 애플리케이션의 코드 수정 등 추가 설정 없이 동작
- containerized workloads as well as more traditional workloads such as virtual machines and standard Linux processes. → VM/서버도 모니터링 가능
- By leveraging Linux eBPF, Cilium retains the ability to transparently insert security visibility + enforcement, but does so in a way that is based on service / pod / container identity (in contrast to IP address identification in traditional systems) and can filter on application-layer (e.g. HTTP). → 전통적인 IP 기반은 모니터링/통제가 아니라 서비스/파드/ID 기반으로 모니터링/통제를 제공
- 기본적으로 Hubble API는 Cilium 에이전트가 실행되는 개별 노드의 범위 내에서 작동합니다. 이는 네트워크 통찰력을 로컬 Cilium 에이전트가 관찰한 트래픽으로 제한합니다. Hubble CLI(
hubble)를 사용하여 로컬 Unix Domain Socket을 통해 제공된 Hubble API를 쿼리할 수 있습니다. Hubble CLI 바이너리는 기본적으로 Cilium 에이전트 포드에 설치됩니다. - Hubble Relay를 배포하면 전체 클러스터 또는 ClusterMesh 시나리오의 여러 클러스터에 대한 네트워크 가시성이 제공됩니다. 이 모드에서 Hubble 데이터는 Hubble CLI(
hubble)를 Hubble Relay 서비스로 지정하거나 Hubble UI를 통해 액세스할 수 있습니다. Hubble UI는 L3/L4 및 L7 계층에서 서비스 종속성 그래프를 자동으로 검색할 수 있는 웹 인터페이스로, 사용자 친화적인 시각화 및 서비스 맵으로서의 데이터 흐름 필터링을 허용합니다. - Metrics export via Prometheus: Key metrics are exported via Prometheus for integration with your existing dashboards.
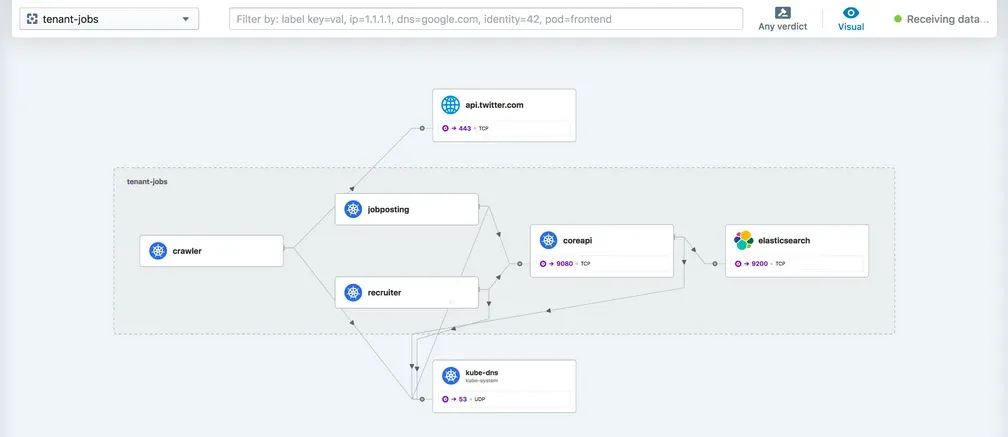
- 서비스 종속성 그래프
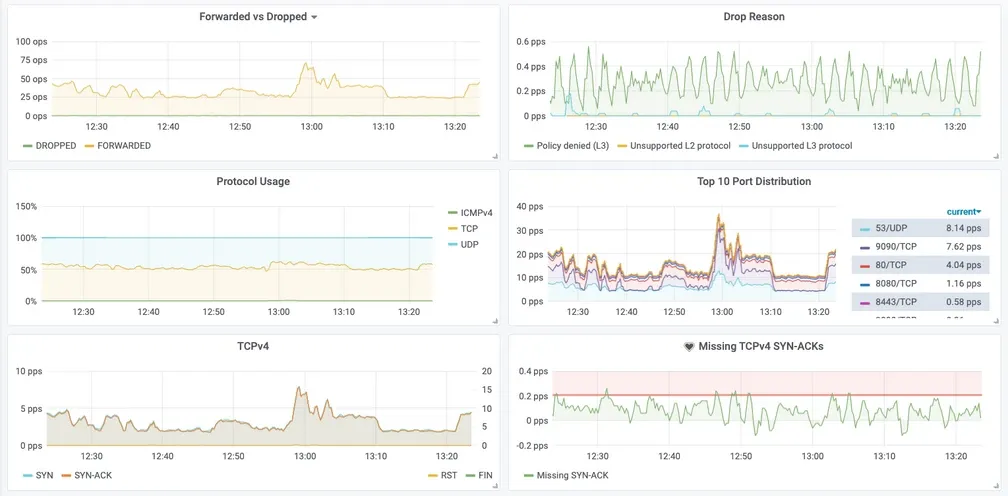
- 다양한 메트릭(네트워크, HTTP, DNS 등) 모니터링
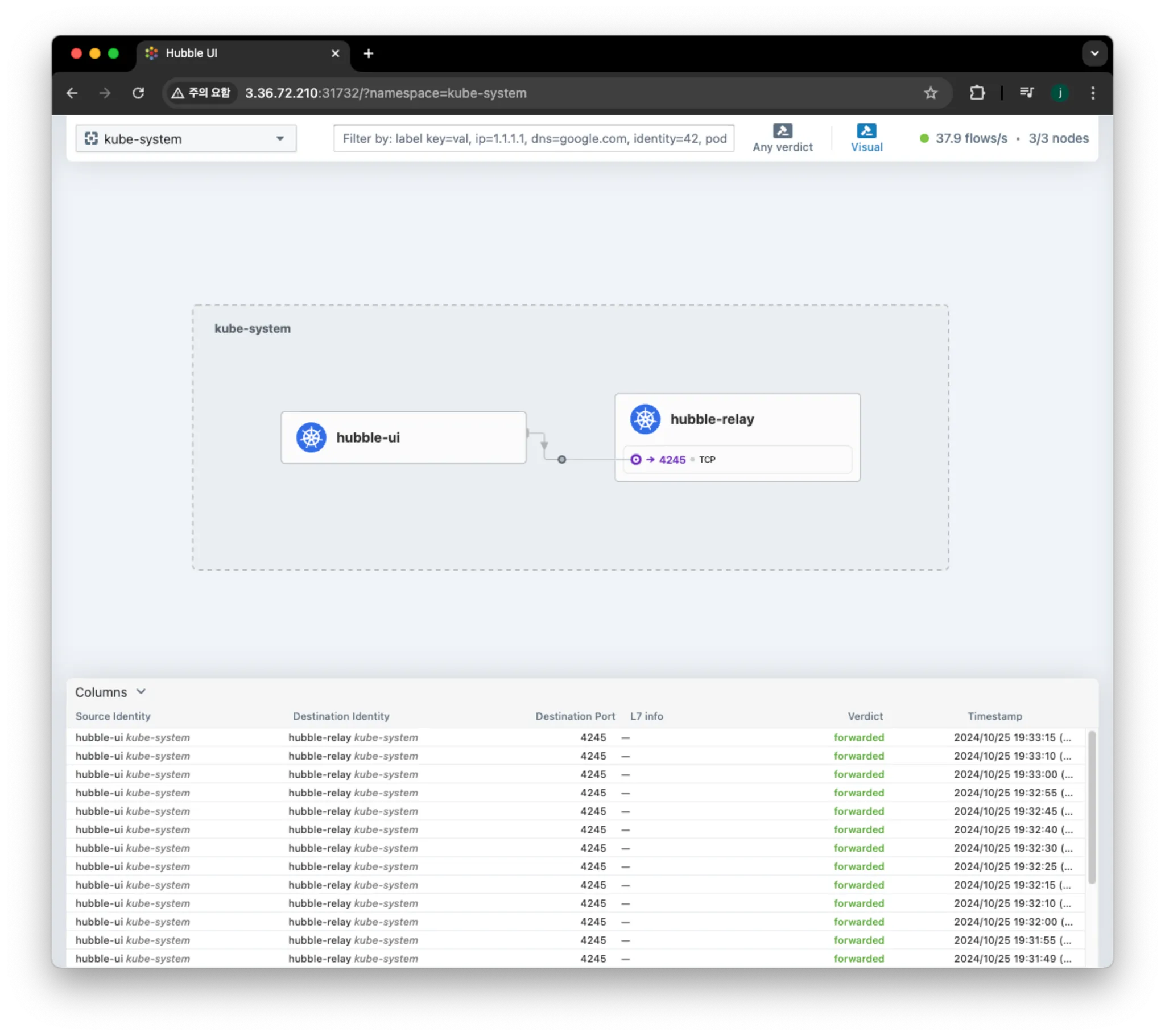
Hubble UI/CLI 접근 및 확인
# 확인
cilium status
# UI 파드 정보 확인
kubectl get pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=hubble-ui -o wide
# Hubble UI 웹 접속
kubectl patch -n kube-system svc hubble-ui -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
HubbleUiNodePort=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system hubble-ui -o jsonpath={.spec.ports[0].nodePort})
echo -e "Hubble UI URL = http://$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip):$HubbleUiNodePort"
## Service NodePort 생성 후 아래 정보 확인!
iptables -t nat -S
conntrack -L
conntrack -L |grep -v 2379
# Install Hubble Client
HUBBLE_VERSION=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/hubble/master/stable.txt)
HUBBLE_ARCH=amd64
if [ "$(uname -m)" = "aarch64" ]; then HUBBLE_ARCH=arm64; fi
curl -L --fail --remote-name-all https://github.com/cilium/hubble/releases/download/$HUBBLE_VERSION/hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
sha256sum --check hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256sum
sudo tar xzvfC hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz /usr/local/bin
rm hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
# Hubble API Access : localhost TCP 4245 Relay 를 통해 접근, observe 를 통해서 flow 쿼리 확인 가능!
cilium hubble port-forward &
# CLI 로 Hubble API 상태 확인
hubble status
# query the flow API and look for flows
hubble observe
# hubble observe --pod netpod
# hubble observe --namespace galaxy --http-method POST --http-path /v1/request-landing
# hubble observe --pod deathstar --protocol http
# hubble observe --pod deathstar --verdict DROPPED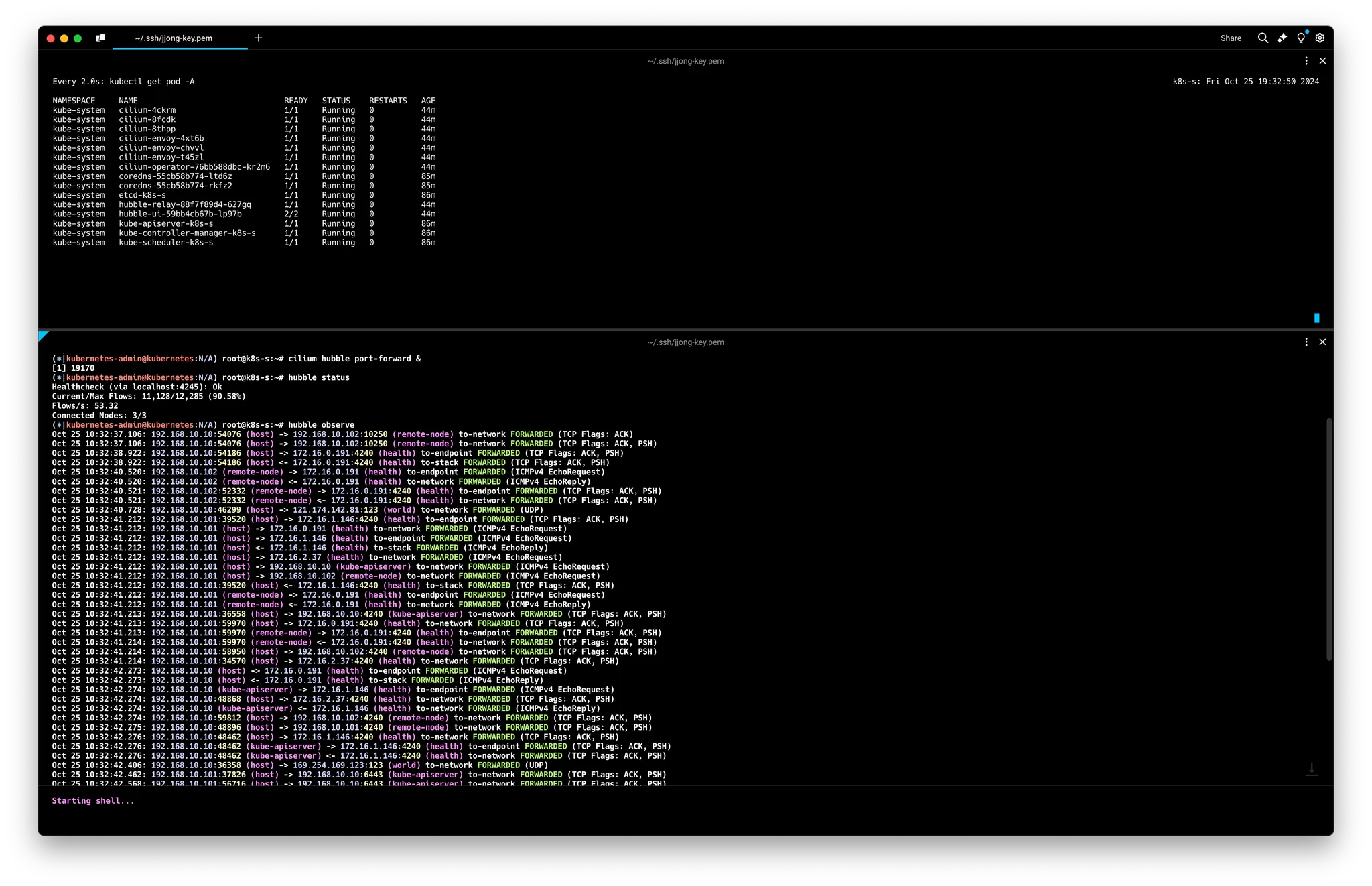
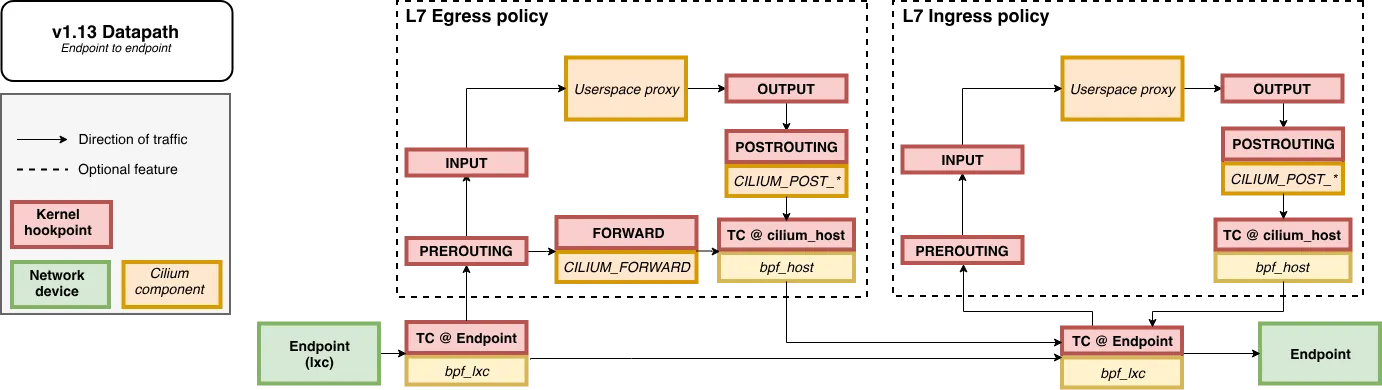
3. 노드 간 파드 통신 확인
Packet Flow
- Endpoint to Endpoint
- Egress from Endpoint
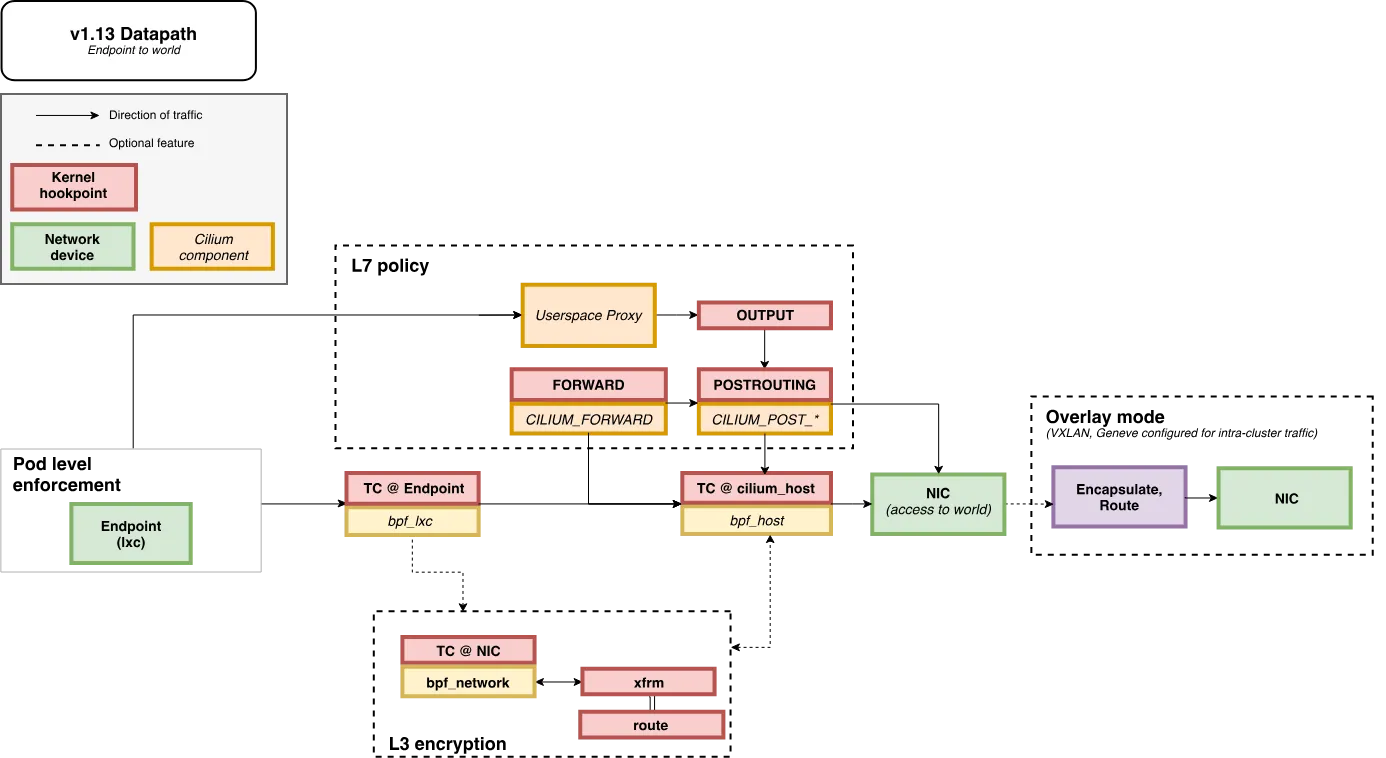
- Ingress to Endpoint
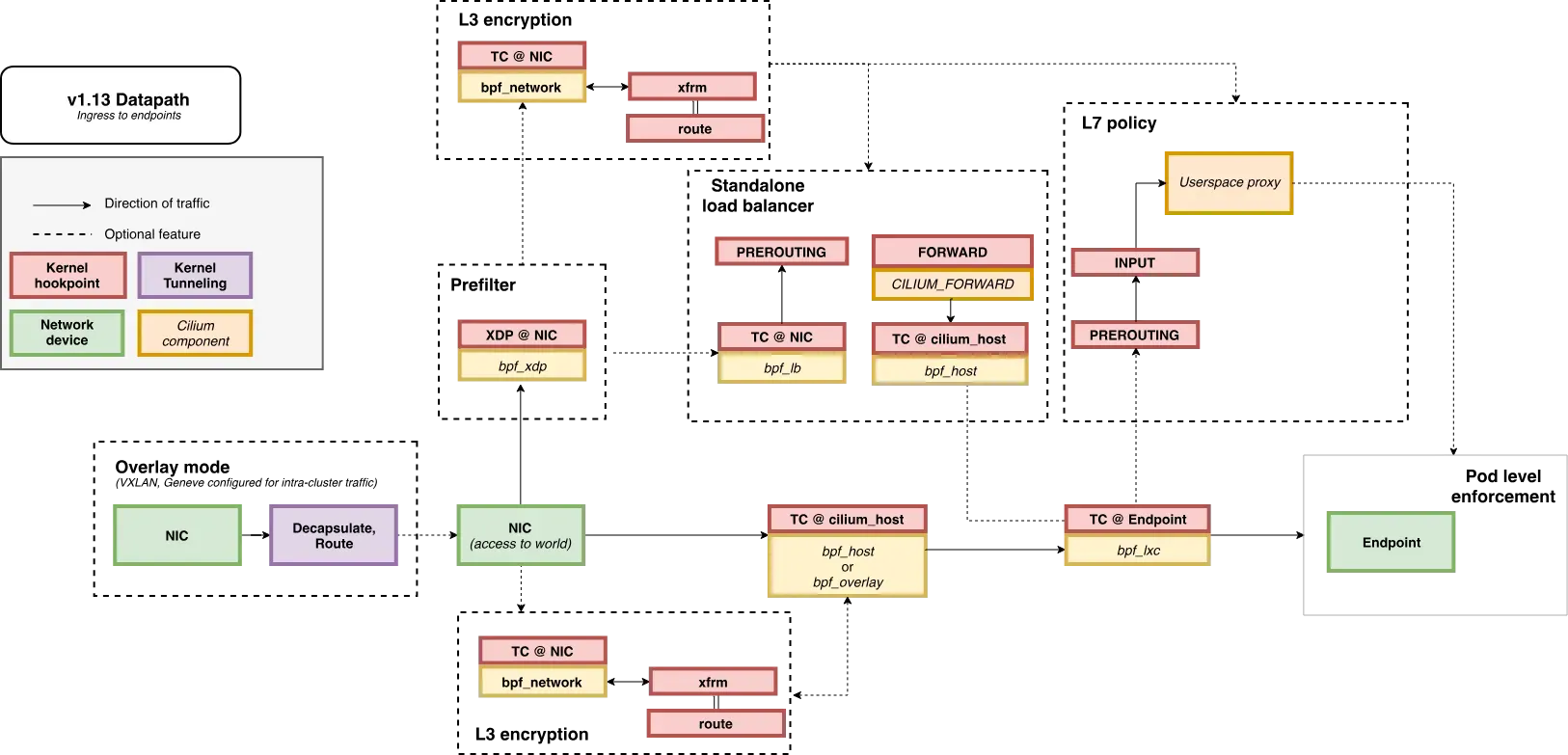
파드 생성 및 확인
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: netpod
labels:
app: netpod
spec:
nodeName: k8s-s
containers:
- name: netshoot-pod
image: nicolaka/netshoot
command: ["tail"]
args: ["-f", "/dev/null"]
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: webpod1
labels:
app: webpod
spec:
nodeName: k8s-w1
containers:
- name: container
image: traefik/whoami
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: webpod2
labels:
app: webpod
spec:
nodeName: k8s-w2
containers:
- name: container
image: traefik/whoami
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
EOF# 확인
kubectl get pod -o wide
c0 status --verbose | grep Allocated -A5
c1 status --verbose | grep Allocated -A5
c2 status --verbose | grep Allocated -A5
kubectl get ciliumendpoints
kubectl get ciliumendpoints -A
c0 endpoint list
c0 bpf endpoint list
c0 map get cilium_lxc
c0 ip list
파드 변수 지정
# 테스트 파드들 IP
NETPODIP=$(kubectl get pods netpod -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')
WEBPOD1IP=$(kubectl get pods webpod1 -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')
WEBPOD2IP=$(kubectl get pods webpod2 -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')
# 단축키(alias) 지정
alias p0="kubectl exec -it netpod -- "
alias p1="kubectl exec -it webpod1 -- "
alias p2="kubectl exec -it webpod2 -- "
파드 ARP 동작 확인
# netpod 네트워크 정보 확인
p0 ip -c -4 addr
p0 route -n
p0 ping -c 1 $WEBPOD1IP && p0 ping -c 1 $WEBPOD2IP
p0 curl -s $WEBPOD1IP && p0 curl -s $WEBPOD2IP
p0 curl -s $WEBPOD1IP:8080 ; p0 curl -s $WEBPOD2IP:8080
p0 ping -c 1 8.8.8.8 && p0 curl -s wttr.in/seoul
p0 ip -c neigh
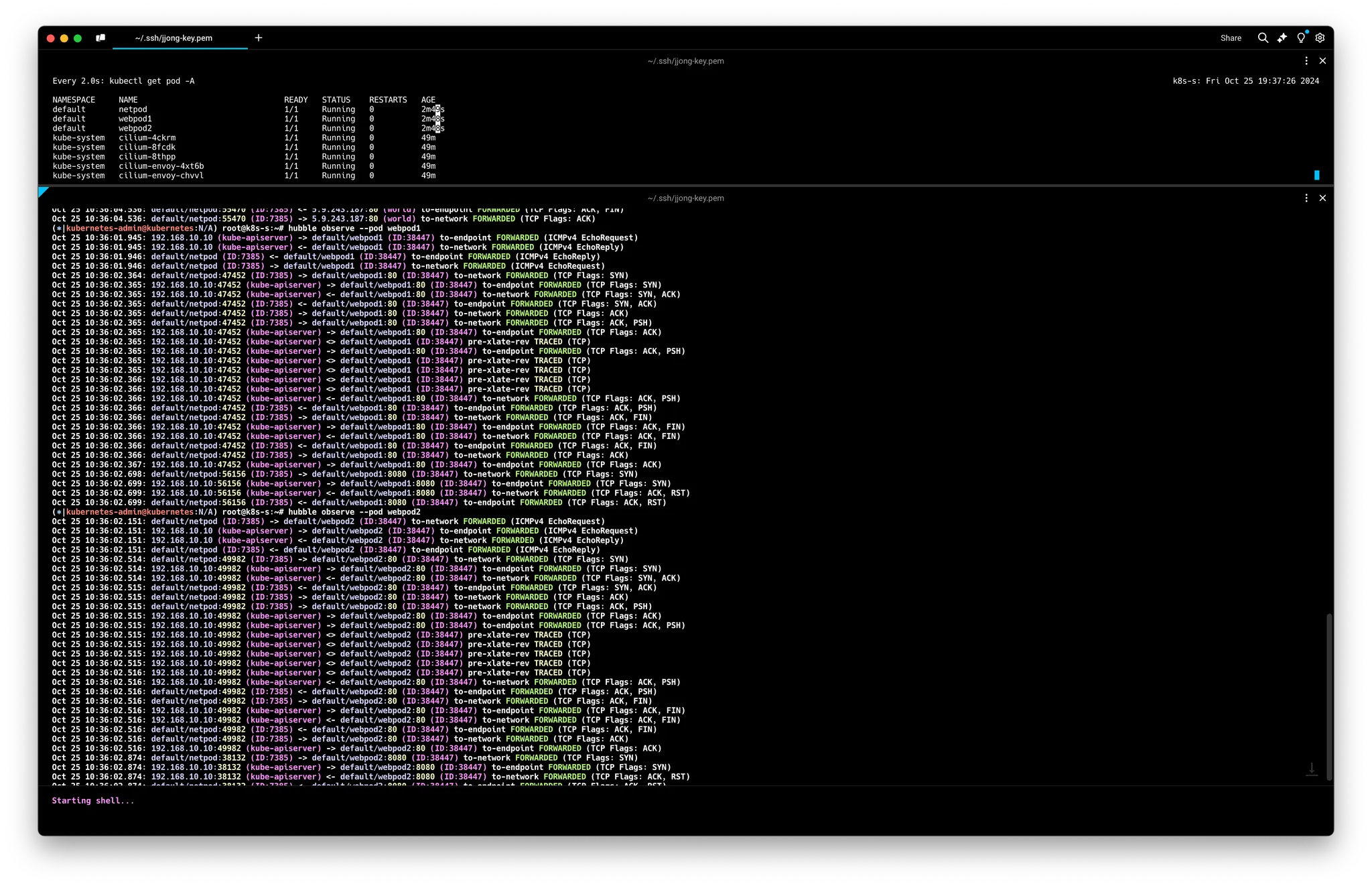
# hubble cli 확인
hubble observe --pod netpod
hubble observe --pod webpod1
hubble observe --pod webpod2
# BPF maps : 목적지 파드와 통신 시 어느곳으로 보내야 될지 확인할 수 있다
c0 map get **cilium_ipcache**
c0 map get cilium_ipcache | grep $WEBPOD1IP
# netpod 의 LXC 변수 지정
LXC=<k8s-s의 가장 나중에 lxc 이름>
LXC=*lxc335e04832afa*
# 파드와 veth pair 에 IP가 없다! proxy_arp 도 없다! 하지만 GW MAC 요청 시 lxc(veth)의 MAC 으로 응답이 온다! >> **eBPF Magic!**
# Cilium **hijacks ARP** table of POD1, forces the next hop to be the peer end (host side) of the veth pair.
ip -c addr show dev $LXC
- Node’s eBPF programs
# list of eBPF programs
**c0bpf net show**
c0bpf net show | grep $LXC
*lxc335e04832afa(12) tcx/ingress **cil_from_container** **prog_id 1529** link_id 26
lxc335e04832afa(12) tcx/egress **cil_to_container** **prog_id 1531** link_id 27*
# Use **bpftool prog show id** to view additional information about a program, including a list of **attached eBPF maps**:
c0bpf prog show id <출력된 prog id 입력>
c0bpf prog show id **1529**
*1531: sched_cls name cil_to_container tag 3f1e92871a2c4013 gpl
loaded_at 2024-10-20T07:47:27+0000 uid 0
xlated 1712B jited 1015B memlock 4096B **map_ids 66,239**
btf_id 474*
****
c0bpf map list
*...
**66**: percpu_hash name cilium_metrics flags 0x1
key 8B value 16B max_entries 1024 memlock 19384B
...
**239**: prog_array name cilium_calls_00 flags 0x0
key 4B value 4B max_entries 50 memlock 720B
owner_prog_type sched_cls owner jited
...*
4. 서비스 통신 확인
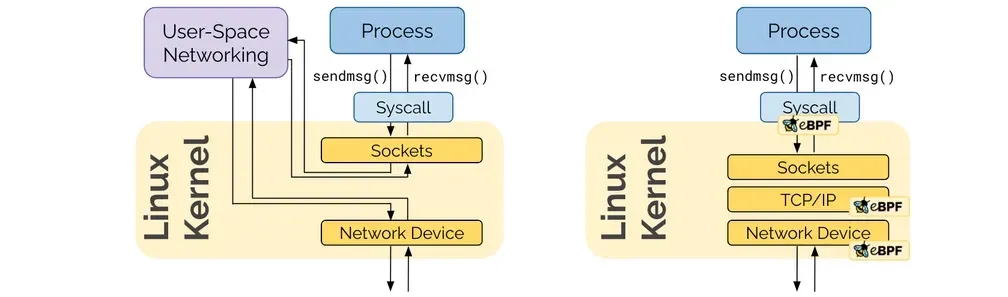
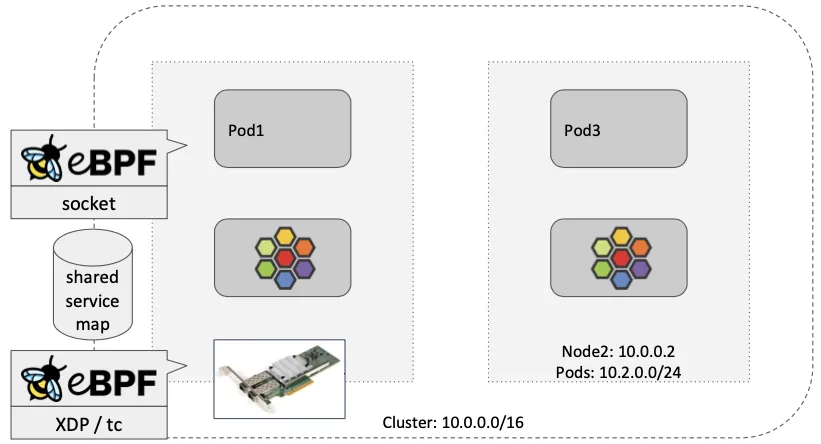
Socket-Based LoadBalancing
- 그림 왼쪽(네트워크 기반 로드밸런싱) vs 오른쪽(소켓 기반 로드밸런싱)
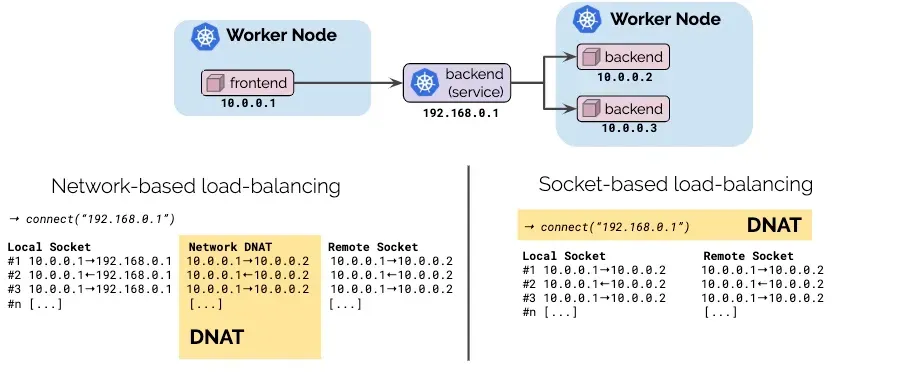
- Pod1 안에서 동작하는 앱이 connect() 시스템콜을 이용하여 소켓을 연결할 때 목적지 주소가 서비스 주소(10.10.8.55)이면 소켓의 목적지 주소를 바로 백엔드 주소(10.0.0.31)로 설정한다. 이후 앱에서 해당 소켓을 통해 보내는 모든 패킷의 목적지 주소는 이미 백엔드 주소(10.0.0.31)로 설정되어 있기 때문에 중간에 DNAT 변환 및 역변환 과정이 필요없어진다.
- destination NAT translation happens at the syscall level, before the packet is even built by the kernel.
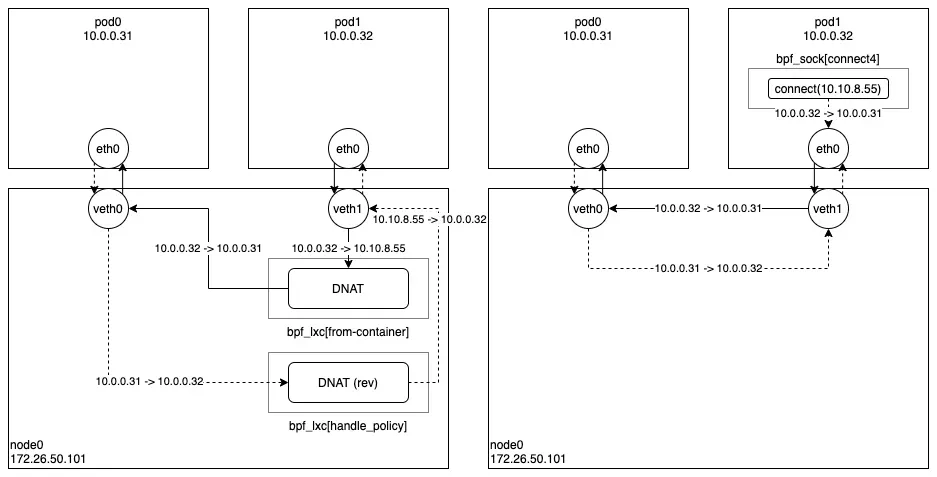
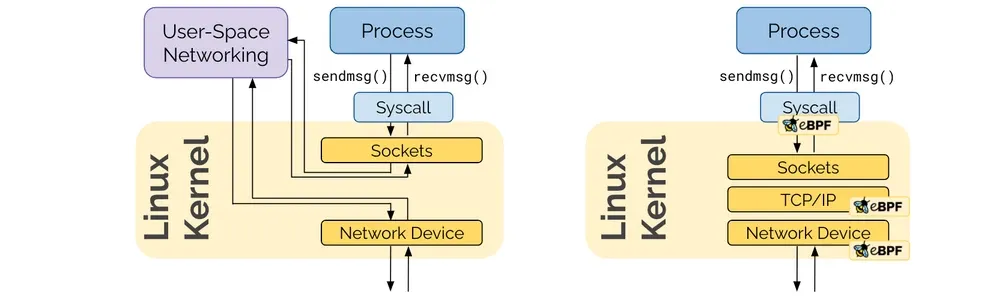
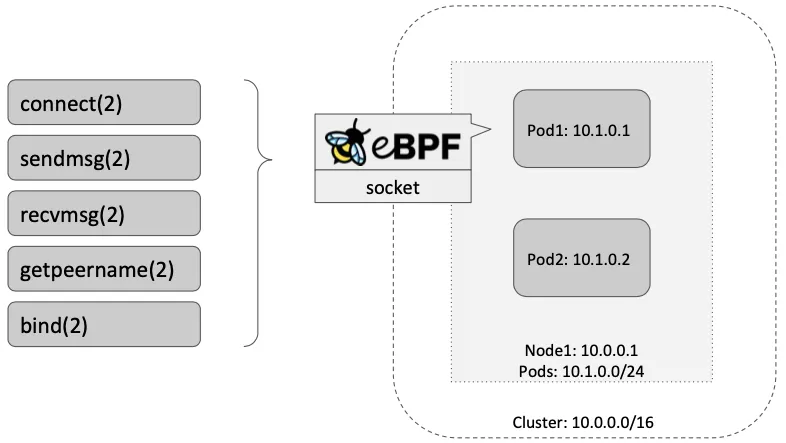
- Socket operations : BPF socket operations program 은 root cgroup 에 연결되며 TCP event(ESTABLISHED) 에서 실행한다.
- Socket send/recv : The socket send/recv hook 은 TCP socket 의 모든 송수신 작업에서 실행, hook 에서 검사/삭제/리다이렉션을 할 수 있다
- connect() 와 sendto() 소켓 함수에 연결된 프로그램(connect4, sendmsg4)에서는 소켓의 목적지 주소를 백엔드 주소와 포트로 변환하고, cilium_lb4_backends 맵에 백엔드 주소와 포트를 등록해놓는다. 이후 recvmsg() 소켓 함수에 연결된 프로그램(recvmsg4)에서는 cilium_lb4_reverse_nat 맵을 이용해서 목적지 주소와 포트를 다시 서비스 주소와 포트로 변환함.
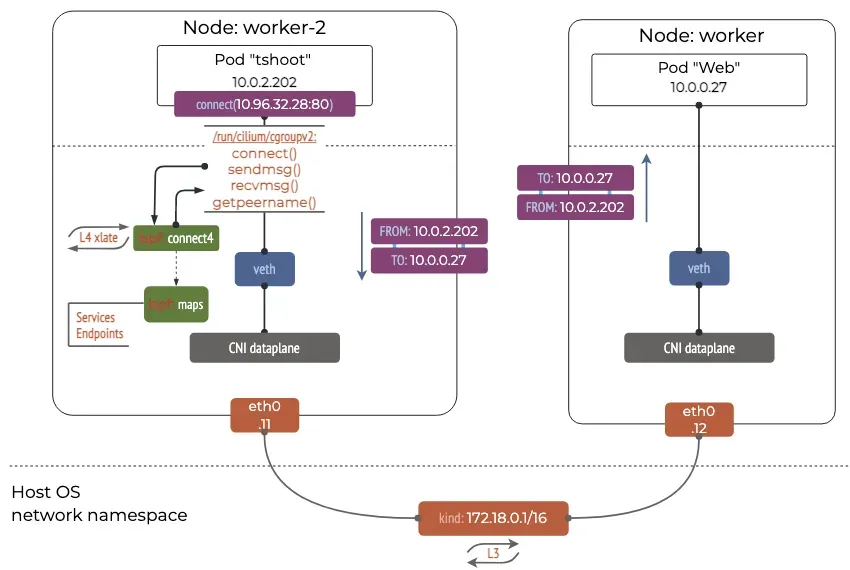
서비스 생성 및 접속확인: Pod 내부에서 직접 DNAT
- 서비스 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: svc
spec:
ports:
- name: svc-webport
port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: webpod
type: ClusterIP
EOF- 서비스 접속 확인
# 서비스 생성 확인
kubectl get svc,ep svc
# 노드에 iptables 더이상 KUBE-SVC rule 이 생성되지 않는다!
iptables-save | grep KUBE-SVC
iptables-save | grep CILIUM
# 서비스IP를 변수에 지정
SVCIP=$(kubectl get svc svc -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterIP}')
# Pod1 에서 Service(ClusterIP) 접속 트래픽 발생
kubectl exec netpod -- curl -s $SVCIP
kubectl exec netpod -- curl -s $SVCIP | grep Hostname
# 지속적으로 접속 트래픽 발생
SVCIP=$(kubectl get svc svc -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterIP}')
while true; do kubectl exec netpod -- curl -s $SVCIP | grep Hostname;echo "-----";sleep 1;done
# 파드에서 SVC(ClusterIP) 접속 시 tcpdump 로 확인 >> **파드 내부 캡쳐**인데, SVC(10.108.12.195)는 보이지 않고, **DNAT 된 web-pod 의 IP**가 확인! **Magic**!
**kubectl exec netpod -- tcpdump -enni any -q**
08:54:55.454271 eth0 Out ifindex 14 92:1a:b9:94:94:37 172.16.0.162.44718 > **172.16.1.234**.80: tcp 0
08:54:55.454798 eth0 In ifindex 14 8a:0c:cc:a9:21:1a 172.16.1.234.80 > 172.16.0.162.44718: tcp 0
08:54:55.455030 eth0 Out ifindex 14 92:1a:b9:94:94:37 172.16.0.162.44718 > **172.16.1.234**.80: tcp 77
...
**kubectl exec netpod --** sh -c "**ngrep** -tW byline -d **eth0** '' 'tcp port **80**'"
*T 2024/10/20 08:07:36.663329 **172.16.0.132:59964** -> **172.16.1.53:80** [AP] #34
GET / HTTP/1.1.
Host: 10.10.124.15.
User-Agent: curl/8.7.1.
Accept: */*.*
# 서비스 정보 확인
c0 service list
ID Frontend Service Type Backend
16 10.108.12.195:80 ClusterIP 1 => 172.16.2.157:80
2 => 172.16.1.234:80
c0 bpf lb list
SERVICE ADDRESS BACKEND ADDRESS
10.108.12.195:80 0.0.0.0:0 (16) [ClusterIP, non-routable]
172.16.1.234:80 (16)
172.16.2.157:80 (16)
# BPF maps
c0 map list --verbose
c0 map list --verbose | grep lb
**c0 map get cilium_lb4_services_v2**
**c0 map get cilium_lb4_backends_v3
c0 map get cilium_lb4_reverse_nat
c0 map get cilium_lb4_reverse_sk**
**c0 map get cilium_lxc**
**c0 map get cilium_ipcache**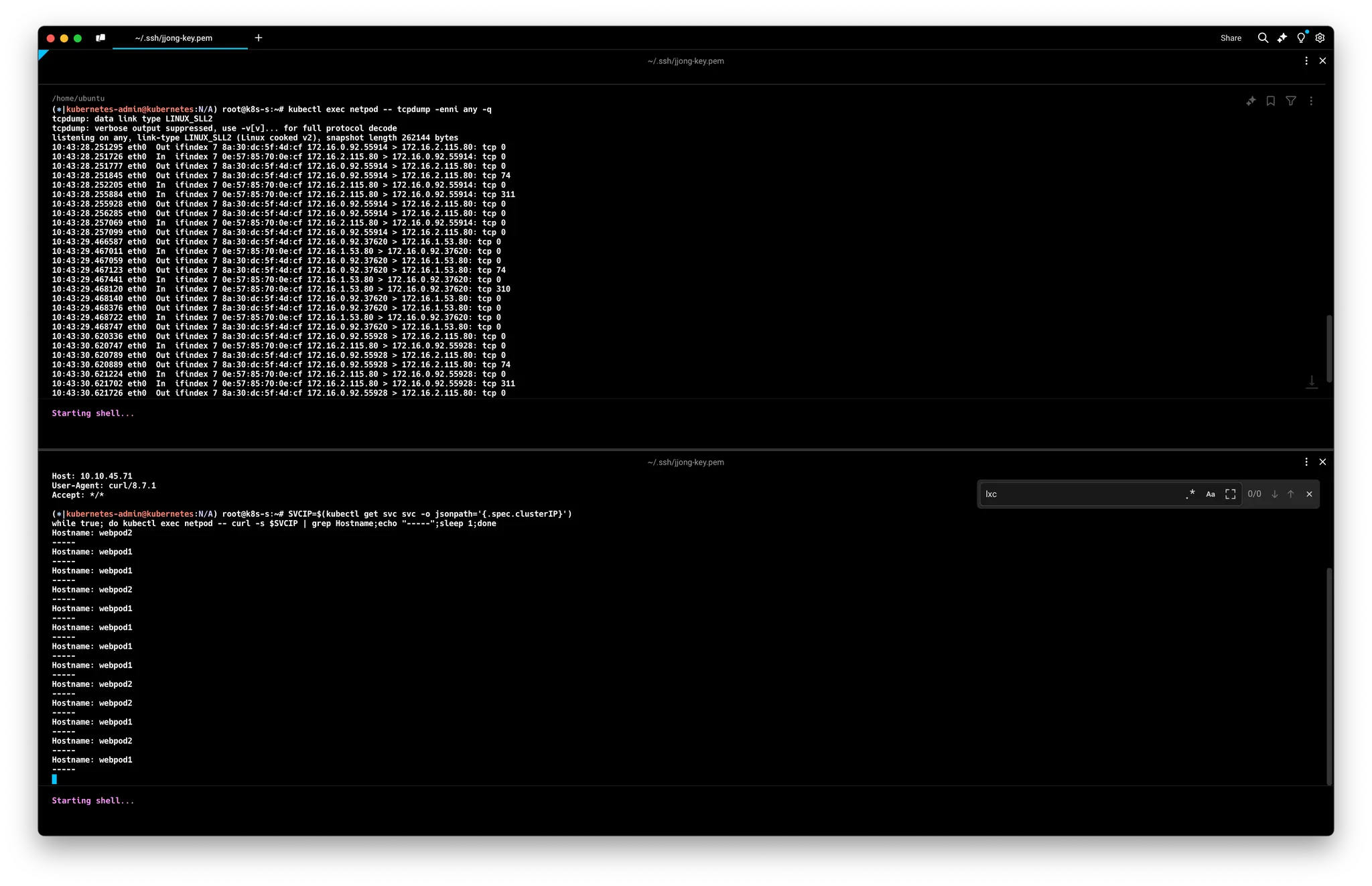
Socket-Based LoadBalancing 관련 설정 값 확인, Cgroup 확인
# Socket-Based LoadBalancing 관련 설정들 확인
c0 status --verbose
...
KubeProxyReplacement Details:
Status: True
Socket LB: Enabled
Socket LB Tracing: Enabled
Socket LB Coverage: Full
Devices: ens5 192.168.10.10 fe80::57:abff:fee3:da8d (Direct Routing)
Mode: SNAT
Backend Selection: Random
Session Affinity: Enabled
Graceful Termination: Enabled
NAT46/64 Support: Disabled
XDP Acceleration: Disabled
Services:
- ClusterIP: Enabled
- NodePort: Enabled (Range: 30000-32767)
- LoadBalancer: Enabled
- externalIPs: Enabled
- HostPort: Enabled
# cgroup root 경로 확인
tree /run/cilium/cgroupv2 -L 1
tree /run/cilium/cgroupv2 -L 2
cilium config view | grep cgroup
cgroup-root /run/cilium/cgroupv2
# eBPF cgroup 확인 : Socket based LB 와 관련
c0bpf cgroup tree
CgroupPath
ID AttachType AttachFlags Name
/sys/fs/cgroup
1081 cgroup_device multi
1498 tcx_ingress cil_to_host
1501 tcx_egress cil_from_host
# cilium 파드의 Init Containers 에서 cgroup 마운트!
Init Containers:
mount-cgroup:
Container ID: containerd://72e9d2ee9731e3536c893f9daaa7674809638e3d137f9eb0f46fe916c2aa2839
Image: quay.io/cilium/cilium:v1.16.3@sha256:62d2a09bbef840a46099ac4c69421c90f84f28d018d479749049011329aa7f28
Image ID: quay.io/cilium/cilium@sha256:62d2a09bbef840a46099ac4c69421c90f84f28d018d479749049011329aa7f28
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Command:
sh
-ec
cp /usr/bin/cilium-mount /hostbin/cilium-mount;
nsenter --cgroup=/hostproc/1/ns/cgroup --mount=/hostproc/1/ns/mnt "${BIN_PATH}/cilium-mount" $CGROUP_ROOT;
rm /hostbin/cilium-mount
State: Terminated
Reason: Completed
Exit Code: 0
Started: Sun, 20 Oct 2024 15:45:34 +0900
Finished: Sun, 20 Oct 2024 15:45:34 +0900
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment:
CGROUP_ROOT: /run/cilium/cgroupv2
BIN_PATH: /opt/cni/bin
Mounts:
/hostbin from cni-path (rw)
/hostproc from hostproc (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-p6bcr (ro)
# mount-cgroup 로그 확인
kubetail -n kube-system -c mount-cgroup --since 12h
...
[cilium-lnwcr] time="2024-10-20T15:45:52+09:00" level=info msg="Mounted cgroupv2 filesystem at /run/cilium/cgroupv2" subsys=cgroups
[cilium-jmr7d] time="2024-10-20T15:45:33+09:00" level=info msg="Mounted cgroupv2 filesystem at /run/cilium/cgroupv2" subsys=cgroups
...- 삭제
kubectl delete pod --all && kubectl delete svc svc
5. Running Promeheus & Grafana
배포하기
# 배포
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.16.3/examples/kubernetes/addons/prometheus/monitoring-example.yaml
kubectl get all -n cilium-monitoring
# 파드와 서비스 확인
kubectl get pod,svc,ep -o wide -n cilium-monitoring
# NodePort 설정
kubectl patch svc grafana -n cilium-monitoring -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
kubectl patch svc prometheus -n cilium-monitoring -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
# Grafana 웹 접속
GPT=$(kubectl get svc -n cilium-monitoring grafana -o jsonpath={.spec.ports[0].nodePort})
echo -e "Grafana URL = http://$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip):$GPT"
# Prometheus 웹 접속 정보 확인
PPT=$(kubectl get svc -n cilium-monitoring prometheus -o jsonpath={.spec.ports[0].nodePort})
echo -e "Prometheus URL = http://$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip):$PPT"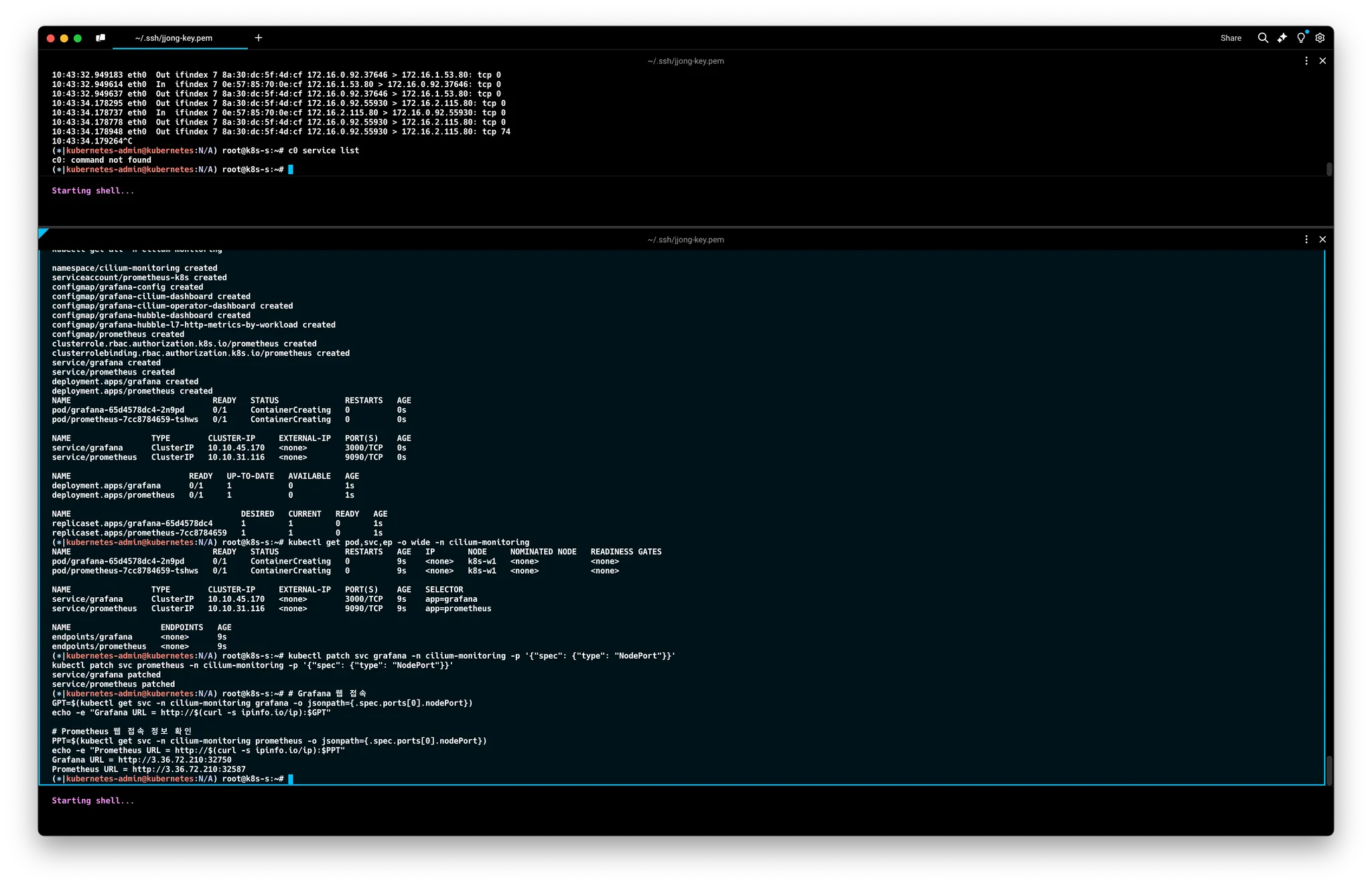
7. Network Policy(L3, L4, L7)
Cilium Security Intro
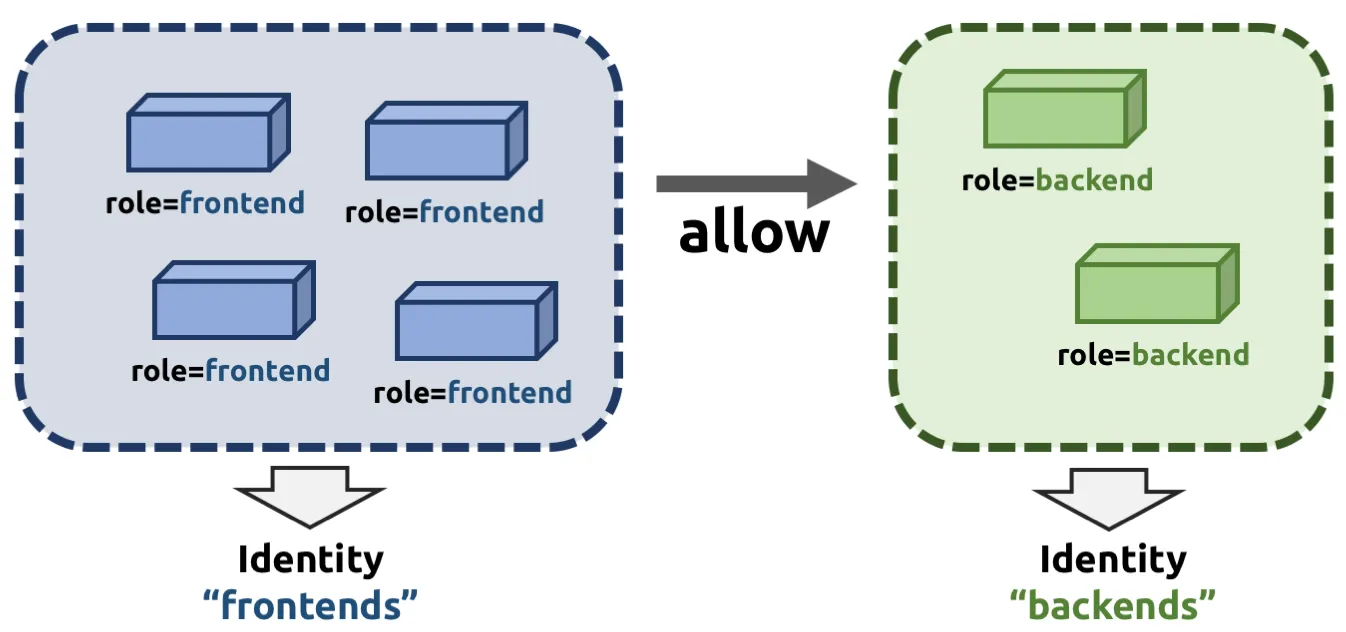
- ID 기반 Identity-Based: Connectivity policies between endpoints (Layer 3), e.g. any endpoint with label
role=frontendcan connect to any endpoint with labelrole=backend.
- 포트 기반 Restriction of accessible ports (Layer 4) for both incoming and outgoing connections, e.g. endpoint with label
role=frontendcan only make outgoing connections on port 443 (https) and endpointrole=backendcan only accept connections on port 443 (https). - 애플리케이션 (HTTP)기반 Fine grained access control on application protocol level to secure HTTP and remote procedure call (RPC) protocols, e.g the endpoint with label
role=frontendcan only perform the REST API callGET /userdata/[0-9]+, all other API interactions withrole=backendare restricted.- Proxy Injection : Envoy - Docs , Envoy
- Cilium is capable of transparently injecting a Layer 4 proxy into any network connection. This is used as the foundation to enforce higher level network policies (see DNS based and Layer 7 Examples).
- Proxy Injection : Envoy - Docs , Envoy
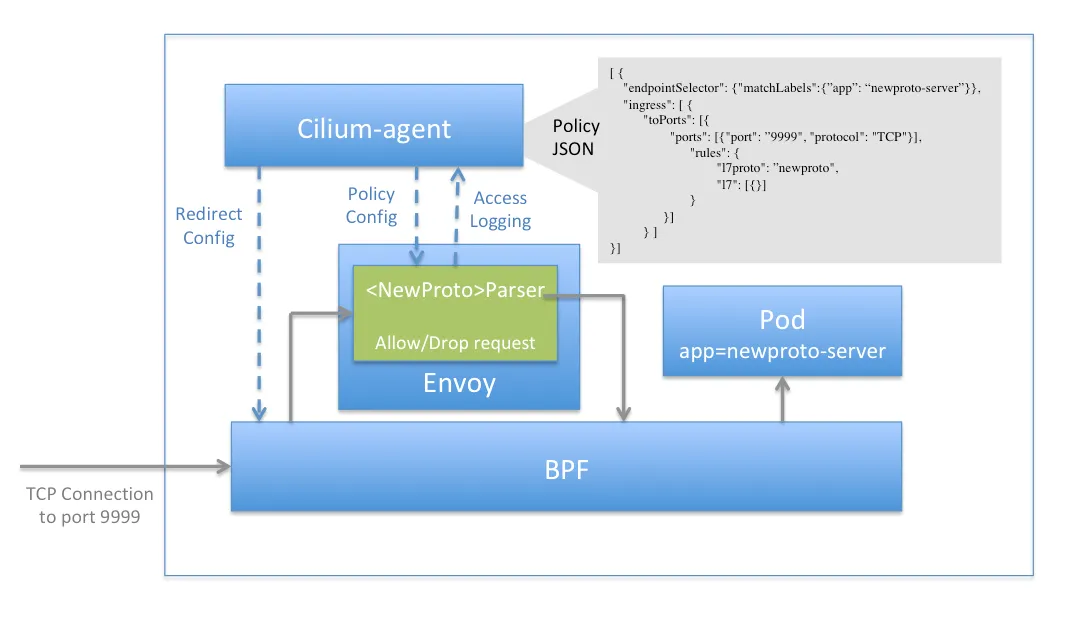
NETWORK POLICY 관련 eBPF Datapath
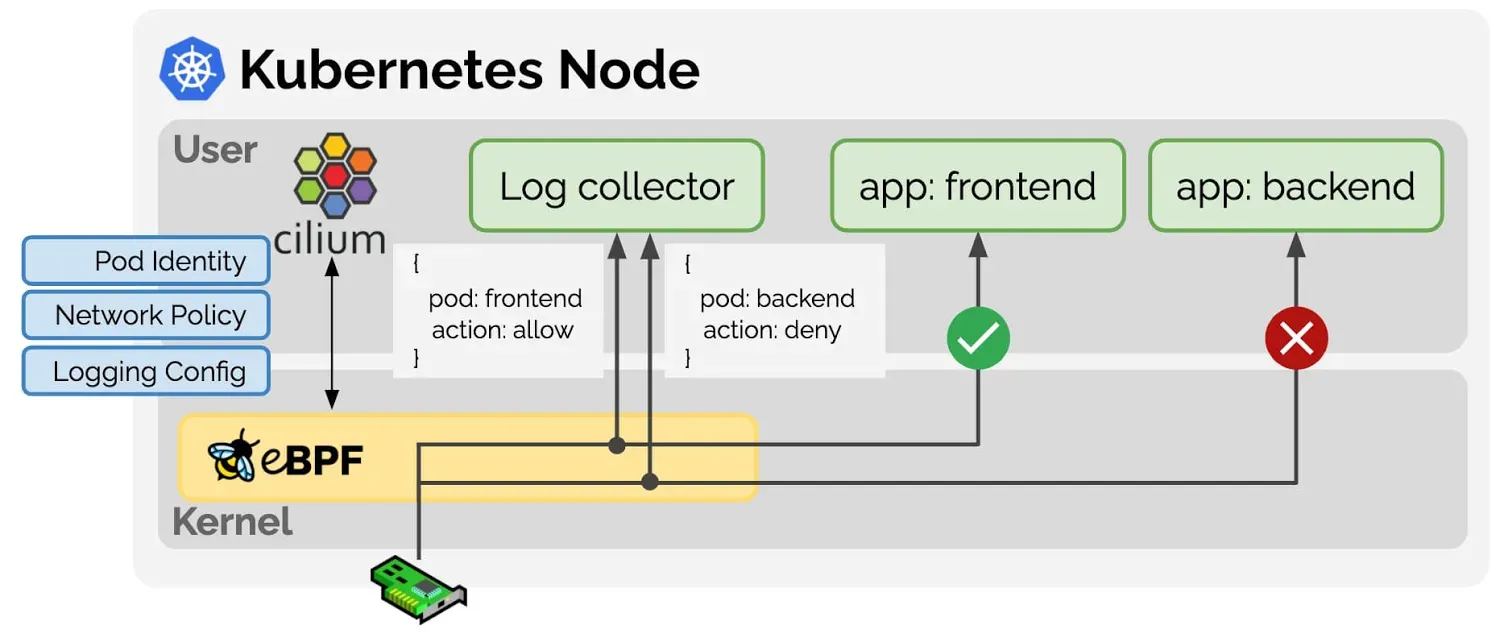
- Prefilter: An XDP program and provides a set of prefilter rules used to filter traffic from the network for best performance.
- Endpoint Policy: 정책에 따라 패킷을 차단/전달하거나, 서비스로 전달하거나, L7 로 정책 전달 할 수 있다.
- the Cilium datapath responsible for mapping packets to identities and enforcing L3 and L4 policies.
- L7 Policy: The L7 Policy object redirect proxy traffic to a Cilium userspace proxy instance. Cilium uses an Envoy instance as its userspace proxy. Envoy will then either forward the traffic or generate appropriate reject messages based on the configured L7 policy.
- → L7 정책는 커널 hookpoint 와 Userspace Proxy 사용으로 성능이 조금 떨어질 수 있다
Demo Application
# 배포
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.16.3/examples/minikube/http-sw-app.yaml
kubectl get all
# 파드 라벨 확인
kubectl get pod --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
deathstar-689f66b57d-4rwkf 1/1 Running 0 113s app.kubernetes.io/name=deathstar,class=deathstar,org=empire,pod-template-hash=689f66b57d
deathstar-689f66b57d-8p2l5 1/1 Running 0 113s app.kubernetes.io/name=deathstar,class=deathstar,org=empire,pod-template-hash=689f66b57d
tiefighter 1/1 Running 0 113s app.kubernetes.io/name=tiefighter,class=tiefighter,org=empire
xwing 1/1 Running 0 113s app.kubernetes.io/name=xwing,class=xwing,org=alliance
# cilium endpoint 확인
kubectl get ciliumendpoints
c1 endpoint list
c2 endpoint list
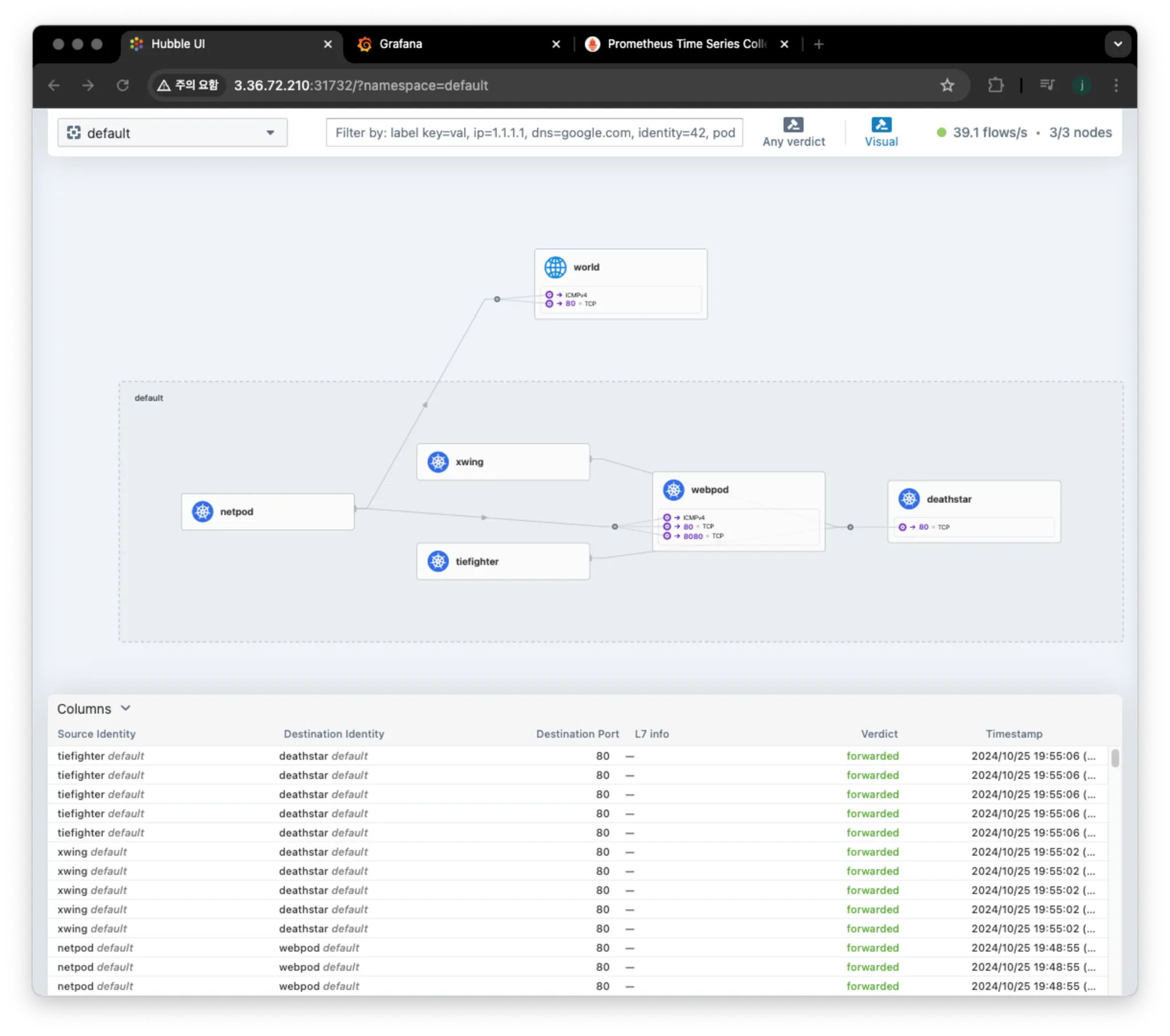
# 데스스타 SVC(ClusterIP) 접속하여 웹 파드 연결 확인 >> Hubble UI 에서 실시간 확인해보자!
kubectl exec xwing -- curl -s -XPOST deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/request-landing
Ship landed
kubectl exec tiefighter -- curl -s -XPOST deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/request-landing
Ship landed
# 확인
hubble observe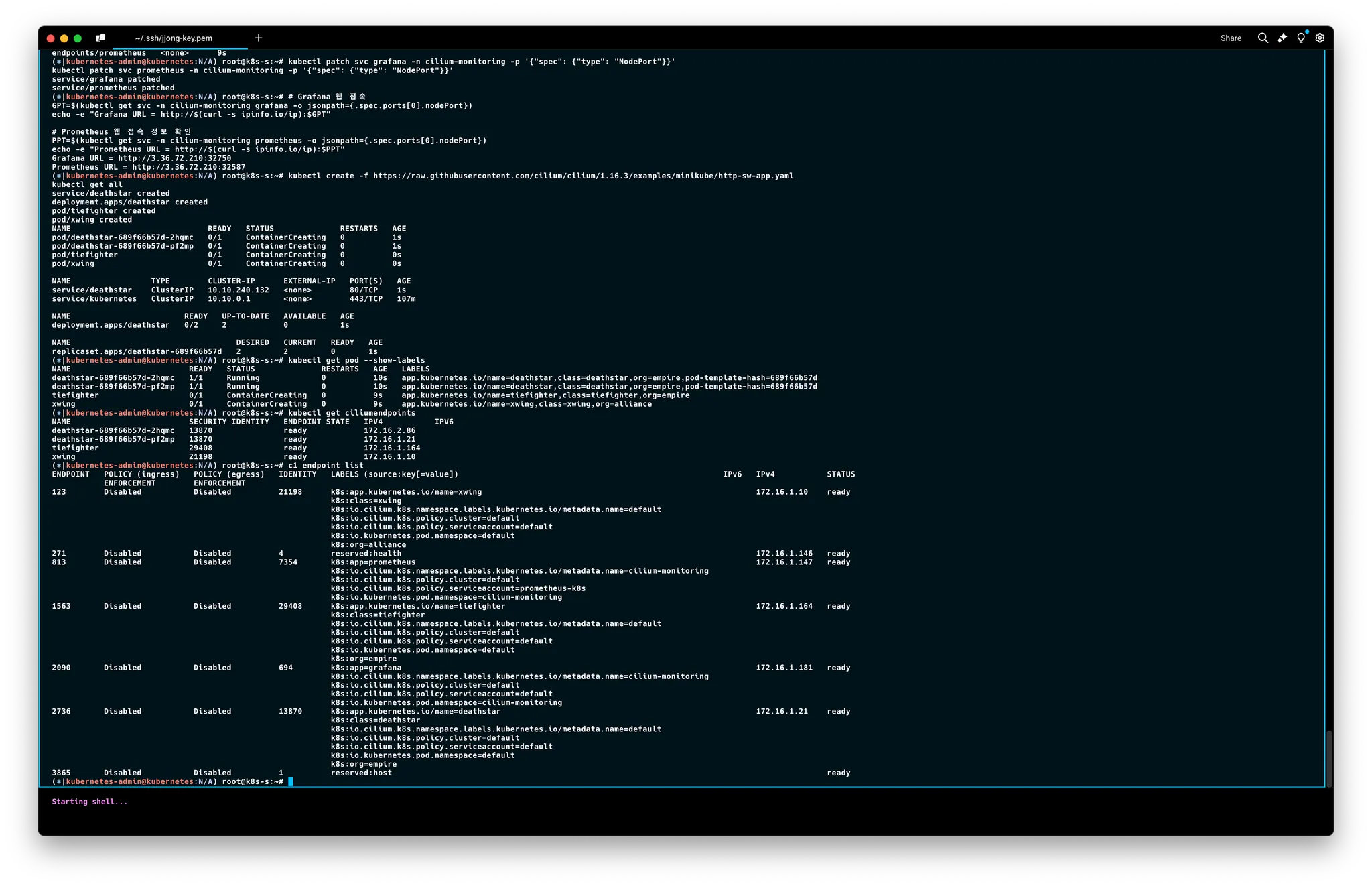
Identity-Aware and HTTP-Aware Policy Enforcement Apply an L3/L4 Policy - Link & Hubble CLI
- Cilium 에서는 Endpoint IP 대신, 파드의 Labels(라벨)을 사용(기준)하여 보안 정책을 적용합니다
- IP/Port 필터링을 L3/L4 네트워크 정책이라고 한다
- 아래 처럼 'org=empire' Labels(라벨) 부착된 파드만 허용해보자
- Cilium performs stateful connection tracking 이므로 리턴 트래픽은 자동으로 허용됨
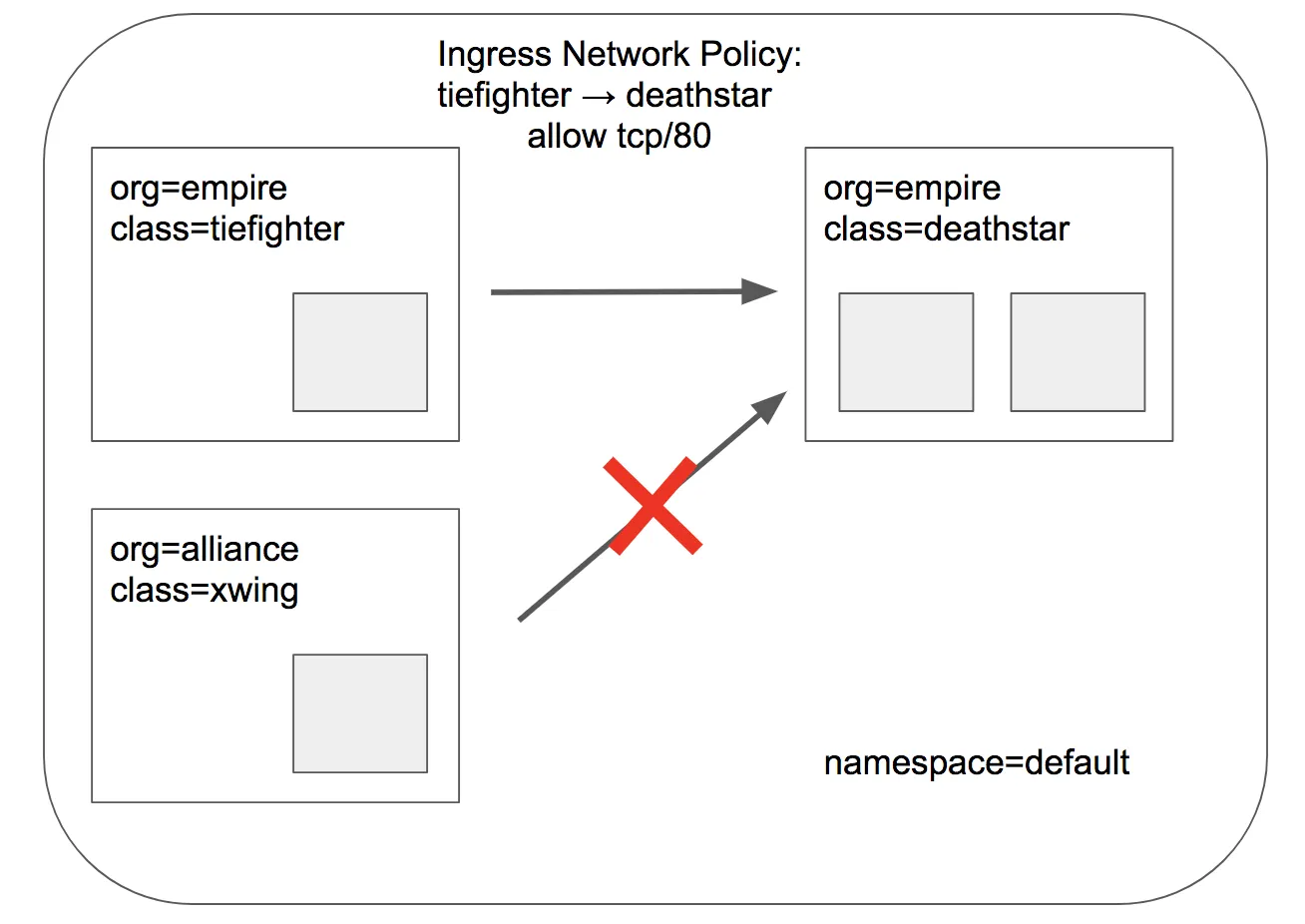
# L3/L4 정책 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: **CiliumNetworkPolicy**
metadata:
name: "rule1"
spec:
description: "L3-L4 policy to restrict deathstar access to empire ships only"
endpointSelector:
matchLabels:
org: empire
class: deathstar
ingress:
- fromEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
org: empire
toPorts:
- ports:
- port: "80"
protocol: TCP
EOF
# 정책 확인
kubectl get cnp
kc describe cnp rule1
c0 policy get
# 파드 curl 접속 시도 시 파드 sh 접속 후 curl 시도하자!
# 데스스타 SVC(ClusterIP) 접속하여 웹 파드 연결 확인 >> Hubble UI 에서 **drop** 확인!
kubectl exec tiefighter -- curl -s -XPOST deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/request-landing
Ship landed
kubectl exec xwing -- curl -s -XPOST deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/request-landing
**drop**
# hubble cli 모니터링
hubble observe --pod xwing
hubble observe --pod tiefighter
hubble observe --pod deathstar
Dec 2 05:36:24.490: default/xwing:55464 <> default/deathstar-c74d84667-t7msh:80 Policy denied DROPPED (TCP Flags: SYN)
Dec 2 05:36:24.490: default/xwing:55464 <> default/deathstar-c74d84667-t7msh:80 Policy denied DROPPED (TCP Flags: SYN)
**hubble observe --pod deathstar --verdict DROPPED**
Nov 30 15:23:47.721: default/xwing:60086 <> default/deathstar-c74d84667-ksnbd:80 Policy denied **DROPPED** (TCP Flags: SYN)
Nov 30 15:23:47.721: default/xwing:60086 <> default/deathstar-c74d84667-ksnbd:80 Policy denied **DROPPED** (TCP Flags: SYN)
Nov 30 15:27:40.250: default/tiefighter:41656 -> default/deathstar-c74d84667-ksnbd:80 http-request **DROPPED** (HTTP/1.1 PUT http://deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/exhaust-port)
Nov 30 15:28:00.707: default/tiefighter:41666 -> default/deathstar-c74d84667-ksnbd:80 http-request **DROPPED** (HTTP/1.1 PUT http://deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/exhaust-port)
**Inspecting the Policy**
# If we run cilium endpoint list again we will see that the pods with the label org=empire and class=deathstar
# now have ingress policy enforcement enabled as per the policy above.
# endpoint list 에서 정책 적용 확인
**c1 endpoint list | grep deathstar**
**c2 endpoint list**
ENDPOINT **POLICY (ingress)** POLICY (egress) IDENTITY LABELS (source:key[=value]) IPv6 IPv4 STATUS
**ENFORCEMENT** ENFORCEMENT
312 Disabled Disabled 18300 k8s:class=xwing 172.16.2.161 ready
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.namespace.labels.kubernetes.io/metadata.name=default
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.cluster=default
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.serviceaccount=default
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=default
k8s:org=alliance
1972 **Enabled** Disabled 21144 **k8s:class=deathstar** 172.16.2.66 ready
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.namespace.labels.kubernetes.io/metadata.name=default
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.cluster=default
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.serviceaccount=default
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=default
k8s:org=empirec2 endpoint list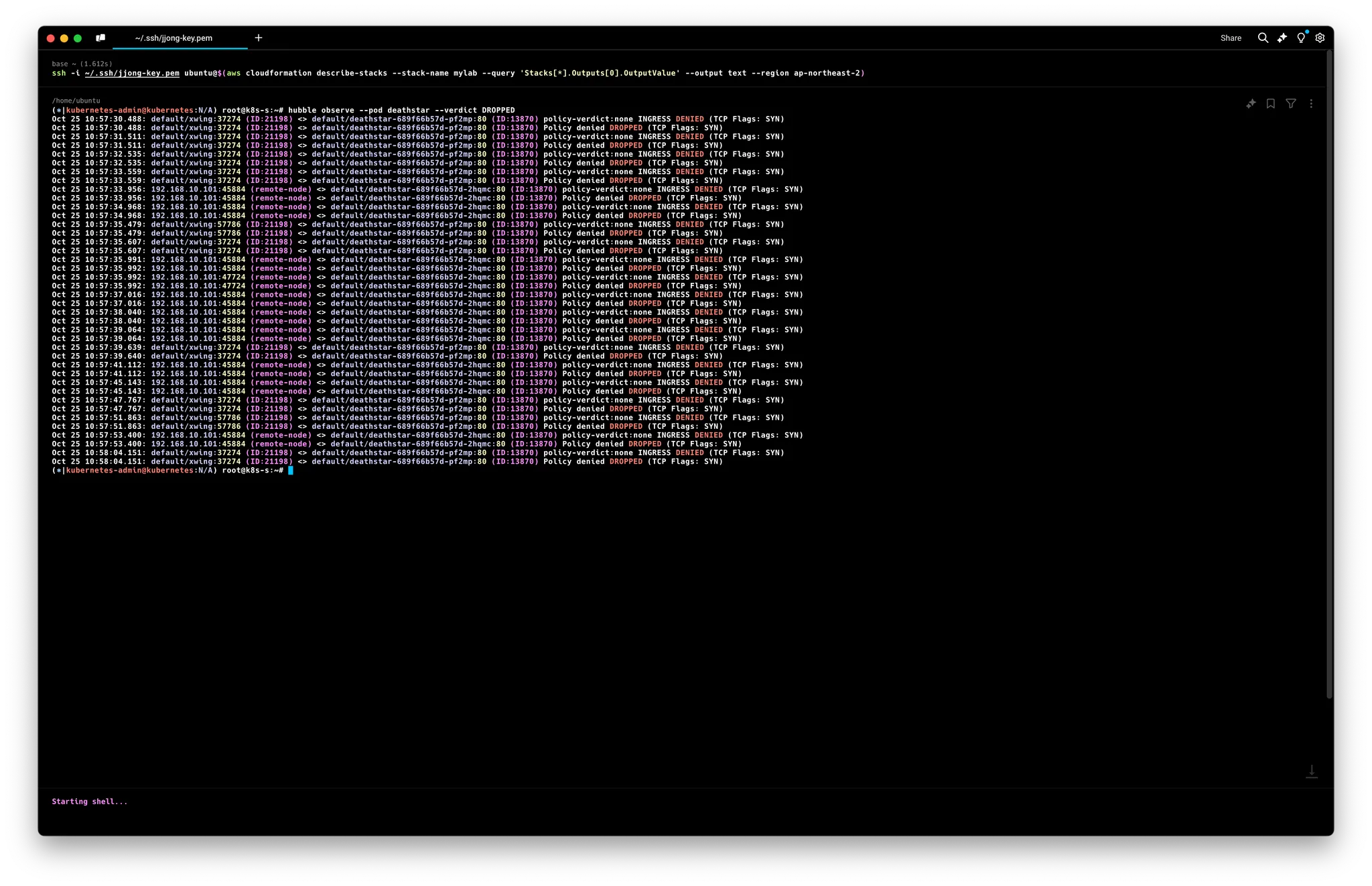
8. BandWidth Manager
설정
# 인터페이스 tc qdisc 확인
tc qdisc show dev ens5
qdisc mq 0: root
qdisc fq_codel 0: parent :4 limit 10240p flows 1024 quantum 1514 target 5ms interval 100ms memory_limit 32Mb ecn drop_batch 64
qdisc fq_codel 0: parent :3 limit 10240p flows 1024 quantum 1514 target 5ms interval 100ms memory_limit 32Mb ecn drop_batch 64
qdisc fq_codel 0: parent :2 limit 10240p flows 1024 quantum 1514 target 5ms interval 100ms memory_limit 32Mb ecn drop_batch 64
qdisc fq_codel 0: parent :1 limit 10240p flows 1024 quantum 1514 target 5ms interval 100ms memory_limit 32Mb ecn drop_batch 64
# 설정
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system --reuse-values --set bandwidthManager.enabled=true
# 적용 확인
cilium config view | grep bandwidth
enable-bandwidth-manager true
# egress bandwidth limitation 동작하는 인터페이스 확인
c0 status | grep BandwidthManager
BandwidthManager: EDT with BPF [CUBIC] [ens5]
# 인터페이스 tc qdisc 확인 : 설정 전후 옵션값들이 상당히 추가된다
tc qdisc
tc qdisc show dev ens5
qdisc mq 8002: root
qdisc fq 8005: parent 8002:2 limit 10000p flow_limit 100p buckets 32768 orphan_mask 1023 quantum 18030b initial_quantum 90150b low_rate_threshold 550Kbit refill_delay 40ms timer_slack 10us horizon 2s horizon_drop
qdisc fq 8003: parent 8002:4 limit 10000p flow_limit 100p buckets 32768 orphan_mask 1023 quantum 18030b initial_quantum 90150b low_rate_threshold 550Kbit refill_delay 40ms timer_slack 10us horizon 2s horizon_drop
qdisc fq 8004: parent 8002:3 limit 10000p flow_limit 100p buckets 32768 orphan_mask 1023 quantum 18030b initial_quantum 90150b low_rate_threshold 550Kbit refill_delay 40ms timer_slack 10us horizon 2s horizon_drop
qdisc fq 8006: parent 8002:1 limit 10000p flow_limit 100p buckets 32768 orphan_mask 1023 quantum 18030b initial_quantum 90150b low_rate_threshold 550Kbit refill_delay 40ms timer_slack 10us horizon 2s horizon_drop
예제 배포
# 테스트를 위한 트래픽 발생 서버/클라이언트 파드 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
annotations:
# Limits egress bandwidth to 10Mbit/s.
kubernetes.io/egress-bandwidth: "10M"
labels:
# This pod will act as server.
app.kubernetes.io/name: netperf-server
name: **netperf-server**
spec:
containers:
- name: netperf
image: cilium/netperf
ports:
- containerPort: 12865
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
# This Pod will act as client.
name: netperf-client
spec:
affinity:
# Prevents the client from being scheduled to the
# same node as the server.
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app.kubernetes.io/name
operator: In
values:
- netperf-server
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
containers:
- name: **netperf**
args:
- sleep
- infinity
image: cilium/netperf
EOF# egress BW 제한 정보 확인
kubectl describe pod netperf-server | grep Annotations:
Annotations: kubernetes.io/egress-bandwidth: 10M
# egress BW 제한이 설정된 파드가 있는 cilium pod 에서 제한 정보 확인
c1 bpf bandwidth list
c2 bpf bandwidth list
IDENTITY EGRESS BANDWIDTH (BitsPerSec)
904 10M
c1 endpoint list
c2 endpoint list
ENDPOINT POLICY (ingress) POLICY (egress) IDENTITY LABELS (source:key[=value]) IPv6 IPv4 STATUS
ENFORCEMENT ENFORCEMENT
904 Disabled Disabled 21565 k8s:app.kubernetes.io/name=netperf-server 172.16.2.153 ready
# 트래픽 발생 >> Hubble UI 에서 확인
# egress traffic of the netperf-server Pod has been limited to 10Mbit per second.
NETPERF_SERVER_IP=$(kubectl get pod netperf-server -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')
kubectl exec netperf-client -- netperf -t TCP_MAERTS -H "${NETPERF_SERVER_IP}"
Recv Send Send
Socket Socket Message Elapsed
Size Size Size Time Throughput
bytes bytes bytes secs. 10^6bits/sec
131072 16384 16384 10.00 9.54 # 10Mbps 제한 확인!
# 5M 제한 설정 후 테스트
kubectl get pod netperf-server -o json | sed -e 's|10M|5M|g' | kubectl apply -f -
c1 bpf bandwidth list
c2 bpf bandwidth list
kubectl exec netperf-client -- netperf -t TCP_MAERTS -H "${NETPERF_SERVER_IP}"
Recv Send Send
Socket Socket Message Elapsed
Size Size Size Time Throughput
bytes bytes bytes secs. 10^6bits/sec
131072 16384 16384 10.09 4.56 # 4.5Mbps 제한 확인!
# 20M 제한 설정 후 테스트
kubectl get pod netperf-server -o json | sed -e 's|5M|20M|g' | kubectl apply -f -
kubectl exec netperf-client -- netperf -t TCP_MAERTS -H "${NETPERF_SERVER_IP}"
Recv Send Send
Socket Socket Message Elapsed
Size Size Size Time Throughput
bytes bytes bytes secs. 10^6bits/sec
131072 16384 16384 10.00 18.95 # 19Mbps 제한 확인!
tc qdisc show dev ens5
# 삭제
kubectl delete pod netperf-client netperf-server⭐ 가시다(gasida) 님이 진행하는 KANS(**K**ubernetes **A**dvanced **N**etworking **S**tudy)3기 실습 게시글입니다.
게시글 상 소스코드, 사진에서 ****굵게**** '''코드쉘''' 에 대한 부분이 들어가있을수도 있습니다.
⭐코드에서 실습 시 사용하는 변수가 들어갈 수 있습니다. 아래의 정보를 사용하고있습니다.
#route53 Domain: jjongguet.com
#AWS Secret Key: jjongkey
#Aws .pem Key: jjong-key.pem
실습 환경 구성
구성 : VPC 1개(퍼블릭 서브넷 2개), EC2 인스턴스 3대 (Ubuntu 22.04 LTS, t3.xlarge - vCPU 4 , Mem 16) , testpc 1대는 t3.small
- CloudFormation 스택 실행 시 파라미터를 기입하면, 해당 정보가 반영되어 배포됩니다.
- CloudFormation 에 EC2의 UserData 부분(Script 실행)으로 실습 환경에 필요한 기본 설정들이 자동으로 진행됩니다.
CloudFormation 스택 배포 ← 실행하는 PC에 aws cli 설치되어 있고, aws configure 자격증명 설정 상태
- 설치 옵션 :
kubeadm init ... **--skip-phases=addon/kube-proxy**
# YAML 파일 다운로드
curl -O https://s3.ap-northeast-2.amazonaws.com/cloudformation.cloudneta.net/kans/**kans-8w.yaml**
# CloudFormation 스택 배포
# aws cloudformation deploy --template-file kans-8w.yaml --stack-name mylab --parameter-overrides KeyName=<My SSH Keyname> SgIngressSshCidr=<My Home Public IP Address>/32 --region ap-northeast-2
예시) aws cloudformation deploy --template-file **kans-8w.yaml** --stack-name **mylab** --parameter-overrides KeyName=jjongkey SgIngressSshCidr=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)/32 --region ap-northeast-2
## Tip. 인스턴스 타입 변경 : MyInstanceType=t3.xlarge (vCPU 4, Mem 16)
예시) aws cloudformation deploy --template-file **kans-8w.yaml** --stack-name **mylab** --parameter-overrides **MyInstanceType=t3.xlarge** KeyName=jjongkey SgIngressSshCidr=$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip)/32 --region ap-northeast-2
# CloudFormation 스택 배포 완료 후 작업용 EC2 IP 출력
aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name **mylab** --query 'Stacks[*].**Outputs[0]**.OutputValue' --output text --region ap-northeast-2
# [모니터링] CloudFormation 스택 상태 : 생성 완료 확인
**while true; do
date
AWS_PAGER="" aws cloudformation list-stacks \
--stack-status-filter CREATE_IN_PROGRESS CREATE_COMPLETE CREATE_FAILED DELETE_IN_PROGRESS DELETE_FAILED \
--query "StackSummaries[*].{StackName:StackName, StackStatus:StackStatus}" \
--output table
sleep 1
done**
# 배포된 aws ec2 유동 공인 IP 확인
**aws ec2 describe-instances --query "Reservations[*].Instances[*].{PublicIPAdd:PublicIpAddress,InstanceName:Tags[?Key=='Name']|[0].Value,Status:State.Name}" --filters Name=instance-state-name,Values=running --output text**
# EC2 SSH 접속 : 바로 접속하지 말고, 5~7분 정도 후에 접속 할 것
ssh -i *~/.ssh/jjong-key.pem* **ubuntu**@$(aws cloudformation describe-stacks --stack-name **mylab** --query 'Stacks[*].Outputs[0].OutputValue' --output text --region ap-northeast-2)
...
*(⎈|kubernetes-admin@kubernetes:N/A) root@k8s-s:~# <- kubeps 가 나오지 않을 경우 ssh logout 후 다시 ssh 접속 할 것!*EC2 생성 수량 부족 실패 시: 사용자 계정의 해당 리전에 EC2 최대 갯수 제한 일 경우, Service Quotas (EC2) 증설 요청으로 해결 - 링크 EC2 요청- Limit Type(EC2 Instances) ⇒ 서울 리전, All Standard (A, C, D, H, I, M, R, T, Z) Instances, New limit value(40 정도)
IP정보

1. Cillium?
LInux Network Stack 의 단점
리눅스 네트워크스택은 복잡하게 구성되어있는데

리눅스 네트워크 스택의 단점은 복잡하고, 변경에 시간이 걸리며, 레이어를 건너뛰기 어렵다는점이다.

1.1 BPF/eBPF ?
BPF(Barkeley Packet Filter) Kernel hooks: BPF는 커널에 삽입하여 패킷을 필터링 할 수 있으며, 다양한 영역에서 Hook을 통해서 접근가능하다.

eBPF는 extended BPF 로써, BPF를 다양한 영역(보안,추적,네트워킹, 모니터링) 에서 활용하기 시작했으며
커널 내의 (샌드박스 내에서) 자유롭게 프로그래밍하여 적용 가능합니다.

1.2 Cilium
Cilium 은 eBPF 를 기반으로 Pod Network환경+보안을 제공하는 CNI PLUGIN 이며
Linux 컨테이너 관리 플랫폼을 사용하여 배포된 응용 프로그램 서비스 간의 네트워크 및 API 연결을 제공하는 오픈 소스 소프트웨어이다.

추가적인 App이나 설정변경없이 Linux Kenral을 자유롭게 프로그래밍해서 동작가능

모든패킷을 가로채기 위해서 NIC의 ingress TC hooks를 사용하는 특징이 있다.
TC: Kernal 에서 동작하는 패킷 스케쥴러

네트워크 모드: 터널모드(VXLAN, GENEVE), Native 라우팅 모드 를 제공

현재 Cilium은 GKE dataplane, EKS Anywhere에서 기본CNI로 사용하고있다.
1.3 Cilium 아키텍쳐
구성요소

- Cilium Agent : 데몬셋으로 실행, K8S API 설정으로 부터 '네트워크 설정, 네트워크 정책, 서비스 부하분산, 모니터링' 등을 수행하며, eBPF 프로그램을 관리한다.
- Cilium Client (CLI) : Cilium 커멘드툴, eBPF maps 에 직접 접속하여 상태를 확인할 수 있다.
- Cilium Operator : K8S 클러스터에 대한 한 번씩 처리해야 하는 작업을 관리.
- Hubble : 네트워크와 보안 모니터링 플랫폼 역할을 하여, 'Server, Relay, Client, Graphical UI' 로 구성되어 있다.
- Data Store : Cilium Agent 간의 상태를 저장하고 전파하는 데이터 저장소, 2가지 종류 중 선택(K8S CRDs, Key-Value Store)

2. Cilium 배포
2.1 배포하기
# 모니터링
watch -d kubectl get node,pod -A -owide
#
helm repo add cilium https://helm.cilium.io/
helm repo update
#
helm install cilium cilium/cilium --version 1.16.3 --namespace kube-system \
--set k8sServiceHost=192.168.10.10 --set k8sServicePort=6443 --set debug.enabled=true \
--set rollOutCiliumPods=true --set routingMode=native --set autoDirectNodeRoutes=true \
--set bpf.masquerade=true --set bpf.hostRouting=true --set endpointRoutes.enabled=true \
--set ipam.mode=kubernetes --set k8s.requireIPv4PodCIDR=true --set kubeProxyReplacement=true \
--set ipv4NativeRoutingCIDR=192.168.0.0/16 --set installNoConntrackIptablesRules=true \
--set hubble.ui.enabled=true --set hubble.relay.enabled=true --set prometheus.enabled=true --set operator.prometheus.enabled=true --set hubble.metrics.enableOpenMetrics=true \
--set hubble.metrics.enabled="{dns:query;ignoreAAAA,drop,tcp,flow,port-distribution,icmp,httpV2:exemplars=true;labelsContext=source_ip\,source_namespace\,source_workload\,destination_ip\,destination_namespace\,destination_workload\,traffic_direction}" \
--set operator.replicas=1
## 주요 파라미터 설명
--set debug.enabled=true # cilium 파드에 로그 레벨을 debug 설정
--set autoDirectNodeRoutes=true # 동일 대역 내의 노드들 끼리는 상대 노드의 podCIDR 대역의 라우팅이 자동으로 설정
--set endpointRoutes.enabled=true # 호스트에 endpoint(파드)별 개별 라우팅 설정
--set hubble.relay.enabled=true --set hubble.ui.enabled=true # hubble 활성화
--set ipam.mode=kubernetes --set k8s.requireIPv4PodCIDR=true # k8s IPAM 활용
--set kubeProxyReplacement=true # kube-proxy 없이 (최대한) 대처할수 있수 있게
--set ipv4NativeRoutingCIDR=192.168.0.0/16 # 해당 대역과 통신 시 IP Masq 하지 않음, 보통 사내망 대역을 지정
--set operator.replicas=1 # cilium-operator 파드 기본 1개
--set enableIPv4Masquerade=true --set bpf.masquerade=true # 파드를 위한 Masquerade , 추가로 Masquerade 을 BPF 로 처리 >> enableIPv4Masquerade=true 인 상태에서 추가로 bpf.masquerade=true 적용이 가능
# 설정 및 확인
ip -c addr
kubectl get node,pod,svc -A -owide
iptables -t nat -S
iptables -t filter -S
iptables -t raw -S
iptables -t mangle -S
conntrack -L
kubectl get crd
kubectl get ciliumnodes # cilium_host 인터페이스의 IP 확인 : CILIUMINTERNALIP
kubectl get ciliumendpoints -A
kubectl get cm -n kube-system cilium-config -o json | jq
kubetail -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium --since 1h
kubetail -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy --since 1h
# Native XDP 지원 NIC 확인 : https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/bpf/progtypes/#xdp-drivers
ethtool -i ens5
driver: ena
version: 6.8.0-1015-aws
...
# https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/operations/performance/tuning/#bypass-iptables-connection-tracking
watch -d kubectl get pod -A # 모니터링
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system --reuse-values --set installNoConntrackIptablesRules=true
# 확인: 기존 raw 에 아래 rule 추가 확인
iptables -t raw -S | grep notrack
-A CILIUM_OUTPUT_raw -d 192.168.0.0/16 -m comment --comment "cilium: NOTRACK for pod traffic" -j CT --notrack
-A CILIUM_OUTPUT_raw -s 192.168.0.0/16 -m comment --comment "cilium: NOTRACK for pod traffic" -j CT --notrack
...
conntrack -F
conntrack -L
conntrack -L |grep -v 2379


Cilium CLI 설치
# Cilium CLI 설치
CILIUM_CLI_VERSION=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium-cli/main/stable.txt)
CLI_ARCH=amd64
if [ "$(uname -m)" = "aarch64" ]; then CLI_ARCH=arm64; fi
curl -L --fail --remote-name-all https://github.com/cilium/cilium-cli/releases/download/${CILIUM_CLI_VERSION}/cilium-linux-${CLI_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
sha256sum --check cilium-linux-${CLI_ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256sum
sudo tar xzvfC cilium-linux-${CLI_ARCH}.tar.gz /usr/local/bin
rm cilium-linux-${CLI_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
# 확인
cilium status --wait
cilium config view
# cilium 데몬셋 파드 내에서 cilium 명령어로 상태 확인
export CILIUMPOD0=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-s -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
alias c0="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD0 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
c0 status --verbose
...
KubeProxyReplacement: True [ens5 192.168.10.10 fe80::57:abff:fee3:da8d (Direct Routing)]
...
IPAM: IPv4: 2/254 allocated from 172.16.0.0/24,
Allocated addresses:
172.16.0.159 (router)
172.16.0.171 (health)
...
Routing: Network: Native Host: BPF
...
Device Mode: veth
Masquerading: BPF [ens5] 192.168.0.0/16 [IPv4: Enabled, IPv6: Disabled]
...
Proxy Status: OK, ip 172.16.0.159, 0 redirects active on ports 10000-20000, Envoy: external
...
KubeProxyReplacement Details:
Status: True
Socket LB: Enabled
Socket LB Tracing: Enabled
Socket LB Coverage: Full
Devices: ens5 192.168.10.10 fe80::57:abff:fee3:da8d (Direct Routing)
Mode: SNAT
Backend Selection: Random
Session Affinity: Enabled
Graceful Termination: Enabled
NAT46/64 Support: Disabled
XDP Acceleration: Disabled
Services:
- ClusterIP: Enabled
- NodePort: Enabled (Range: 30000-32767)
- LoadBalancer: Enabled
- externalIPs: Enabled
- HostPort: Enabled
BPF Maps: dynamic sizing: on (ratio: 0.002500)
...
# Native Routing 확인 : # 192.168.0.0/16 대역은 IP Masq 없이 라우팅
c0 status | grep KubeProxyReplacement
ubeProxyReplacement: True [ens5 192.168.10.10 fe80::57:abff:fee3:da8d (Direct Routing)]
# enableIPv4Masquerade=true(기본값) , bpf.masquerade=true 확인
cilium config view | egrep 'enable-ipv4-masquerade|enable-bpf-masquerade'
enable-bpf-masquerade true
enable-ipv4-masquerade true
c0 status --verbose | grep Masquerading
Masquerading: BPF [ens5] 192.168.0.0/16 [IPv4: Enabled, IPv6: Disabled]
# Configure the eBPF-based ip-masq-agent
# https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/concepts/masquerading/
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system --reuse-values --set ipMasqAgent.enabled=true
#
cilium config view | grep -i masq
enable-bpf-masquerade true
enable-ip-masq-agent true
...
export CILIUMPOD0=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-s -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
alias c0="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD0 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
c0 status --verbose | grep Masquerading
Masquerading: BPF (ip-masq-agent) [ens5] 192.168.0.0/16 [IPv4: Enabled, IPv6: Disabled]
kubectl get cm -n kube-system cilium-config -o yaml | grep ip-masq
enable-ip-masq-agent: "true"

2.2 Cilium 기본 정보 확인
변수& 단축키 확인
# cilium 파드 이름
export CILIUMPOD0=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-s -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
export CILIUMPOD1=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-w1 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
export CILIUMPOD2=$(kubectl get -l k8s-app=cilium pods -n kube-system --field-selector spec.nodeName=k8s-w2 -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
# 단축키(alias) 지정
alias c0="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD0 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
alias c1="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD1 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
alias c2="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD2 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- cilium"
alias c0bpf="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD0 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- bpftool"
alias c1bpf="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD1 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- bpftool"
alias c2bpf="kubectl exec -it $CILIUMPOD2 -n kube-system -c cilium-agent -- bpftool"
# Hubble UI 웹 접속
kubectl patch -n kube-system svc hubble-ui -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
HubbleUiNodePort=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system hubble-ui -o jsonpath={.spec.ports[0].nodePort})
echo -e "Hubble UI URL = http://$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip):$HubbleUiNodePort"
# 자주 사용 명령
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system --reuse-values --set
kubetail -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium --since 12h
kubetail -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium-envoy --since 12h
자주사용하는 Cilium CLI 명령어
# cilium 파드 확인
kubectl get pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium -owide
# cilium 파드 재시작
kubectl -n kube-system rollout restart ds/cilium
혹은
kubectl delete pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=cilium
# cilium 설정 정보 확인
cilium config view
# cilium 파드의 cilium 상태 확인
c0 status --verbose
# cilium 엔드포인트 확인
kubectl get ciliumendpoints -A
c0 endpoint list
c0 bpf endpoint list
c0 map get cilium_lxc
c0 ip list
# Manage the IPCache mappings for IP/CIDR <-> Identity
c0 bpf ipcache list
# Service/NAT List 확인
c0 service list
c0 bpf lb list
c0 bpf lb list --revnat
c0 bpf nat list
# List all open BPF maps
c0 map list
c0 map list --verbose
# List contents of a policy BPF map : Dump all policy maps
c0 bpf policy get --all
c0 bpf policy get --all -n
# cilium monitor
c0 monitor -v
c0 monitor -v --type l7네트워크 기본정보 확인: k8s-w1/w2 에 접속 후 ip -c link/route 정보확인


# 네트워크 인터페이스 정보 확인
ip -br -c link
ip -br -c addr
--------------------------------------------
# cilium_net 과 cilium_host 는 veth peer 관계이며, cilium_host 는 파드의 GW IP 주소로 지정되며 32bit 이다
ip -c addr show cilium_net ; ip -c addr show cilium_host
5: cilium_net@cilium_host: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 36:88:bf:c9:5c:6c brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
...
6: cilium_host@cilium_net: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 4e:6a:8e:44:85:61 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 172.16.1.254/32 scope link cilium_host
...
# proxy arp 는 disable(0) 상태이며, 파드와 연결된 lxc 도 모두 0 이다
# 파드의 32bit ip의 gw 가 각각 연결된 veth 인터페이스의 mac 으로 cilium_host 의 IP/MAC 응답을 처리한다, 어떻게 동작이 되는걸까요? >> eBPF program!!!
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/cilium_net/proxy_arp
0
cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/cilium_host/proxy_arp
0
# lxc_health 인터페이스는 veth 로 cilium(NET NS 0, 호스트와 다름)과 veth pair 이다 - 링크
# cilium 인터페이스에 파드 IP가 할당되어 있으며, cilium-health-responder 로 동작한다
lsns -t net
2.3 Hubble UI & CLI
Hubble: 통신 및 서비스와 네트워킹 인프라의 동작에 대한 심층적인 가시성을 완전히 투명한 방식으로 제공하는 관찰성을 제공
- Hubble is a fully distributed networking and security observability platform. → 네트워크/보안 모니터링
- It is built on top of Cilium and eBPF to enable deep visibility into the communication and behavior of services as well as the networking infrastructure in a completely transparent manner. without requiring the application to change in any way. → 애플리케이션의 코드 수정 등 추가 설정 없이 동작
- containerized workloads as well as more traditional workloads such as virtual machines and standard Linux processes. → VM/서버도 모니터링 가능
- By leveraging Linux eBPF, Cilium retains the ability to transparently insert security visibility + enforcement, but does so in a way that is based on service / pod / container identity (in contrast to IP address identification in traditional systems) and can filter on application-layer (e.g. HTTP). → 전통적인 IP 기반은 모니터링/통제가 아니라 서비스/파드/ID 기반으로 모니터링/통제를 제공
- 기본적으로 Hubble API는 Cilium 에이전트가 실행되는 개별 노드의 범위 내에서 작동합니다. 이는 네트워크 통찰력을 로컬 Cilium 에이전트가 관찰한 트래픽으로 제한합니다. Hubble CLI(
hubble)를 사용하여 로컬 Unix Domain Socket을 통해 제공된 Hubble API를 쿼리할 수 있습니다. Hubble CLI 바이너리는 기본적으로 Cilium 에이전트 포드에 설치됩니다. - Hubble Relay를 배포하면 전체 클러스터 또는 ClusterMesh 시나리오의 여러 클러스터에 대한 네트워크 가시성이 제공됩니다. 이 모드에서 Hubble 데이터는 Hubble CLI(
hubble)를 Hubble Relay 서비스로 지정하거나 Hubble UI를 통해 액세스할 수 있습니다. Hubble UI는 L3/L4 및 L7 계층에서 서비스 종속성 그래프를 자동으로 검색할 수 있는 웹 인터페이스로, 사용자 친화적인 시각화 및 서비스 맵으로서의 데이터 흐름 필터링을 허용합니다. - Metrics export via Prometheus: Key metrics are exported via Prometheus for integration with your existing dashboards.

- 서비스 종속성 그래프

- 다양한 메트릭(네트워크, HTTP, DNS 등) 모니터링

Hubble UI/CLI 접근 및 확인
# 확인
cilium status
# UI 파드 정보 확인
kubectl get pod -n kube-system -l k8s-app=hubble-ui -o wide
# Hubble UI 웹 접속
kubectl patch -n kube-system svc hubble-ui -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
HubbleUiNodePort=$(kubectl get svc -n kube-system hubble-ui -o jsonpath={.spec.ports[0].nodePort})
echo -e "Hubble UI URL = http://$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip):$HubbleUiNodePort"
## Service NodePort 생성 후 아래 정보 확인!
iptables -t nat -S
conntrack -L
conntrack -L |grep -v 2379
# Install Hubble Client
HUBBLE_VERSION=$(curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/hubble/master/stable.txt)
HUBBLE_ARCH=amd64
if [ "$(uname -m)" = "aarch64" ]; then HUBBLE_ARCH=arm64; fi
curl -L --fail --remote-name-all https://github.com/cilium/hubble/releases/download/$HUBBLE_VERSION/hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
sha256sum --check hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz.sha256sum
sudo tar xzvfC hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz /usr/local/bin
rm hubble-linux-${HUBBLE_ARCH}.tar.gz{,.sha256sum}
# Hubble API Access : localhost TCP 4245 Relay 를 통해 접근, observe 를 통해서 flow 쿼리 확인 가능!
cilium hubble port-forward &
# CLI 로 Hubble API 상태 확인
hubble status
# query the flow API and look for flows
hubble observe
# hubble observe --pod netpod
# hubble observe --namespace galaxy --http-method POST --http-path /v1/request-landing
# hubble observe --pod deathstar --protocol http
# hubble observe --pod deathstar --verdict DROPPED

3. 노드 간 파드 통신 확인
Packet Flow
- Endpoint to Endpoint

- Egress from Endpoint

- Ingress to Endpoint

파드 생성 및 확인
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: netpod
labels:
app: netpod
spec:
nodeName: k8s-s
containers:
- name: netshoot-pod
image: nicolaka/netshoot
command: ["tail"]
args: ["-f", "/dev/null"]
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: webpod1
labels:
app: webpod
spec:
nodeName: k8s-w1
containers:
- name: container
image: traefik/whoami
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: webpod2
labels:
app: webpod
spec:
nodeName: k8s-w2
containers:
- name: container
image: traefik/whoami
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0
EOF# 확인
kubectl get pod -o wide
c0 status --verbose | grep Allocated -A5
c1 status --verbose | grep Allocated -A5
c2 status --verbose | grep Allocated -A5
kubectl get ciliumendpoints
kubectl get ciliumendpoints -A
c0 endpoint list
c0 bpf endpoint list
c0 map get cilium_lxc
c0 ip list
파드 변수 지정
# 테스트 파드들 IP
NETPODIP=$(kubectl get pods netpod -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')
WEBPOD1IP=$(kubectl get pods webpod1 -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')
WEBPOD2IP=$(kubectl get pods webpod2 -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')
# 단축키(alias) 지정
alias p0="kubectl exec -it netpod -- "
alias p1="kubectl exec -it webpod1 -- "
alias p2="kubectl exec -it webpod2 -- "
파드 ARP 동작 확인
# netpod 네트워크 정보 확인
p0 ip -c -4 addr
p0 route -n
p0 ping -c 1 $WEBPOD1IP && p0 ping -c 1 $WEBPOD2IP
p0 curl -s $WEBPOD1IP && p0 curl -s $WEBPOD2IP
p0 curl -s $WEBPOD1IP:8080 ; p0 curl -s $WEBPOD2IP:8080
p0 ping -c 1 8.8.8.8 && p0 curl -s wttr.in/seoul
p0 ip -c neigh
# hubble cli 확인
hubble observe --pod netpod
hubble observe --pod webpod1
hubble observe --pod webpod2
# BPF maps : 목적지 파드와 통신 시 어느곳으로 보내야 될지 확인할 수 있다
c0 map get **cilium_ipcache**
c0 map get cilium_ipcache | grep $WEBPOD1IP
# netpod 의 LXC 변수 지정
LXC=<k8s-s의 가장 나중에 lxc 이름>
LXC=*lxc335e04832afa*
# 파드와 veth pair 에 IP가 없다! proxy_arp 도 없다! 하지만 GW MAC 요청 시 lxc(veth)의 MAC 으로 응답이 온다! >> **eBPF Magic!**
# Cilium **hijacks ARP** table of POD1, forces the next hop to be the peer end (host side) of the veth pair.
ip -c addr show dev $LXC

- Node’s eBPF programs
# list of eBPF programs
**c0bpf net show**
c0bpf net show | grep $LXC
*lxc335e04832afa(12) tcx/ingress **cil_from_container** **prog_id 1529** link_id 26
lxc335e04832afa(12) tcx/egress **cil_to_container** **prog_id 1531** link_id 27*
# Use **bpftool prog show id** to view additional information about a program, including a list of **attached eBPF maps**:
c0bpf prog show id <출력된 prog id 입력>
c0bpf prog show id **1529**
*1531: sched_cls name cil_to_container tag 3f1e92871a2c4013 gpl
loaded_at 2024-10-20T07:47:27+0000 uid 0
xlated 1712B jited 1015B memlock 4096B **map_ids 66,239**
btf_id 474*
****
c0bpf map list
*...
**66**: percpu_hash name cilium_metrics flags 0x1
key 8B value 16B max_entries 1024 memlock 19384B
...
**239**: prog_array name cilium_calls_00 flags 0x0
key 4B value 4B max_entries 50 memlock 720B
owner_prog_type sched_cls owner jited
...*
4. 서비스 통신 확인
Socket-Based LoadBalancing
- 그림 왼쪽(네트워크 기반 로드밸런싱) vs 오른쪽(소켓 기반 로드밸런싱)

- Pod1 안에서 동작하는 앱이 connect() 시스템콜을 이용하여 소켓을 연결할 때 목적지 주소가 서비스 주소(10.10.8.55)이면 소켓의 목적지 주소를 바로 백엔드 주소(10.0.0.31)로 설정한다. 이후 앱에서 해당 소켓을 통해 보내는 모든 패킷의 목적지 주소는 이미 백엔드 주소(10.0.0.31)로 설정되어 있기 때문에 중간에 DNAT 변환 및 역변환 과정이 필요없어진다.
- destination NAT translation happens at the syscall level, before the packet is even built by the kernel.

- Socket operations : BPF socket operations program 은 root cgroup 에 연결되며 TCP event(ESTABLISHED) 에서 실행한다.
- Socket send/recv : The socket send/recv hook 은 TCP socket 의 모든 송수신 작업에서 실행, hook 에서 검사/삭제/리다이렉션을 할 수 있다

- connect() 와 sendto() 소켓 함수에 연결된 프로그램(connect4, sendmsg4)에서는 소켓의 목적지 주소를 백엔드 주소와 포트로 변환하고, cilium_lb4_backends 맵에 백엔드 주소와 포트를 등록해놓는다. 이후 recvmsg() 소켓 함수에 연결된 프로그램(recvmsg4)에서는 cilium_lb4_reverse_nat 맵을 이용해서 목적지 주소와 포트를 다시 서비스 주소와 포트로 변환함.

서비스 생성 및 접속확인: Pod 내부에서 직접 DNAT
- 서비스 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: svc
spec:
ports:
- name: svc-webport
port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: webpod
type: ClusterIP
EOF- 서비스 접속 확인
# 서비스 생성 확인
kubectl get svc,ep svc
# 노드에 iptables 더이상 KUBE-SVC rule 이 생성되지 않는다!
iptables-save | grep KUBE-SVC
iptables-save | grep CILIUM
# 서비스IP를 변수에 지정
SVCIP=$(kubectl get svc svc -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterIP}')
# Pod1 에서 Service(ClusterIP) 접속 트래픽 발생
kubectl exec netpod -- curl -s $SVCIP
kubectl exec netpod -- curl -s $SVCIP | grep Hostname
# 지속적으로 접속 트래픽 발생
SVCIP=$(kubectl get svc svc -o jsonpath='{.spec.clusterIP}')
while true; do kubectl exec netpod -- curl -s $SVCIP | grep Hostname;echo "-----";sleep 1;done
# 파드에서 SVC(ClusterIP) 접속 시 tcpdump 로 확인 >> **파드 내부 캡쳐**인데, SVC(10.108.12.195)는 보이지 않고, **DNAT 된 web-pod 의 IP**가 확인! **Magic**!
**kubectl exec netpod -- tcpdump -enni any -q**
08:54:55.454271 eth0 Out ifindex 14 92:1a:b9:94:94:37 172.16.0.162.44718 > **172.16.1.234**.80: tcp 0
08:54:55.454798 eth0 In ifindex 14 8a:0c:cc:a9:21:1a 172.16.1.234.80 > 172.16.0.162.44718: tcp 0
08:54:55.455030 eth0 Out ifindex 14 92:1a:b9:94:94:37 172.16.0.162.44718 > **172.16.1.234**.80: tcp 77
...
**kubectl exec netpod --** sh -c "**ngrep** -tW byline -d **eth0** '' 'tcp port **80**'"
*T 2024/10/20 08:07:36.663329 **172.16.0.132:59964** -> **172.16.1.53:80** [AP] #34
GET / HTTP/1.1.
Host: 10.10.124.15.
User-Agent: curl/8.7.1.
Accept: */*.*
# 서비스 정보 확인
c0 service list
ID Frontend Service Type Backend
16 10.108.12.195:80 ClusterIP 1 => 172.16.2.157:80
2 => 172.16.1.234:80
c0 bpf lb list
SERVICE ADDRESS BACKEND ADDRESS
10.108.12.195:80 0.0.0.0:0 (16) [ClusterIP, non-routable]
172.16.1.234:80 (16)
172.16.2.157:80 (16)
# BPF maps
c0 map list --verbose
c0 map list --verbose | grep lb
**c0 map get cilium_lb4_services_v2**
**c0 map get cilium_lb4_backends_v3
c0 map get cilium_lb4_reverse_nat
c0 map get cilium_lb4_reverse_sk**
**c0 map get cilium_lxc**
**c0 map get cilium_ipcache**
Socket-Based LoadBalancing 관련 설정 값 확인, Cgroup 확인


# Socket-Based LoadBalancing 관련 설정들 확인
c0 status --verbose
...
KubeProxyReplacement Details:
Status: True
Socket LB: Enabled
Socket LB Tracing: Enabled
Socket LB Coverage: Full
Devices: ens5 192.168.10.10 fe80::57:abff:fee3:da8d (Direct Routing)
Mode: SNAT
Backend Selection: Random
Session Affinity: Enabled
Graceful Termination: Enabled
NAT46/64 Support: Disabled
XDP Acceleration: Disabled
Services:
- ClusterIP: Enabled
- NodePort: Enabled (Range: 30000-32767)
- LoadBalancer: Enabled
- externalIPs: Enabled
- HostPort: Enabled
# cgroup root 경로 확인
tree /run/cilium/cgroupv2 -L 1
tree /run/cilium/cgroupv2 -L 2
cilium config view | grep cgroup
cgroup-root /run/cilium/cgroupv2
# eBPF cgroup 확인 : Socket based LB 와 관련
c0bpf cgroup tree
CgroupPath
ID AttachType AttachFlags Name
/sys/fs/cgroup
1081 cgroup_device multi
1498 tcx_ingress cil_to_host
1501 tcx_egress cil_from_host
# cilium 파드의 Init Containers 에서 cgroup 마운트!
Init Containers:
mount-cgroup:
Container ID: containerd://72e9d2ee9731e3536c893f9daaa7674809638e3d137f9eb0f46fe916c2aa2839
Image: quay.io/cilium/cilium:v1.16.3@sha256:62d2a09bbef840a46099ac4c69421c90f84f28d018d479749049011329aa7f28
Image ID: quay.io/cilium/cilium@sha256:62d2a09bbef840a46099ac4c69421c90f84f28d018d479749049011329aa7f28
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
Command:
sh
-ec
cp /usr/bin/cilium-mount /hostbin/cilium-mount;
nsenter --cgroup=/hostproc/1/ns/cgroup --mount=/hostproc/1/ns/mnt "${BIN_PATH}/cilium-mount" $CGROUP_ROOT;
rm /hostbin/cilium-mount
State: Terminated
Reason: Completed
Exit Code: 0
Started: Sun, 20 Oct 2024 15:45:34 +0900
Finished: Sun, 20 Oct 2024 15:45:34 +0900
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment:
CGROUP_ROOT: /run/cilium/cgroupv2
BIN_PATH: /opt/cni/bin
Mounts:
/hostbin from cni-path (rw)
/hostproc from hostproc (rw)
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from kube-api-access-p6bcr (ro)
# mount-cgroup 로그 확인
kubetail -n kube-system -c mount-cgroup --since 12h
...
[cilium-lnwcr] time="2024-10-20T15:45:52+09:00" level=info msg="Mounted cgroupv2 filesystem at /run/cilium/cgroupv2" subsys=cgroups
[cilium-jmr7d] time="2024-10-20T15:45:33+09:00" level=info msg="Mounted cgroupv2 filesystem at /run/cilium/cgroupv2" subsys=cgroups
...- 삭제
kubectl delete pod --all && kubectl delete svc svc
5. Running Promeheus & Grafana
배포하기
# 배포
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.16.3/examples/kubernetes/addons/prometheus/monitoring-example.yaml
kubectl get all -n cilium-monitoring
# 파드와 서비스 확인
kubectl get pod,svc,ep -o wide -n cilium-monitoring
# NodePort 설정
kubectl patch svc grafana -n cilium-monitoring -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
kubectl patch svc prometheus -n cilium-monitoring -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort"}}'
# Grafana 웹 접속
GPT=$(kubectl get svc -n cilium-monitoring grafana -o jsonpath={.spec.ports[0].nodePort})
echo -e "Grafana URL = http://$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip):$GPT"
# Prometheus 웹 접속 정보 확인
PPT=$(kubectl get svc -n cilium-monitoring prometheus -o jsonpath={.spec.ports[0].nodePort})
echo -e "Prometheus URL = http://$(curl -s ipinfo.io/ip):$PPT"


7. Network Policy(L3, L4, L7)
Cilium Security Intro
- ID 기반 Identity-Based: Connectivity policies between endpoints (Layer 3), e.g. any endpoint with label
role=frontendcan connect to any endpoint with labelrole=backend.

- 포트 기반 Restriction of accessible ports (Layer 4) for both incoming and outgoing connections, e.g. endpoint with label
role=frontendcan only make outgoing connections on port 443 (https) and endpointrole=backendcan only accept connections on port 443 (https). - 애플리케이션 (HTTP)기반 Fine grained access control on application protocol level to secure HTTP and remote procedure call (RPC) protocols, e.g the endpoint with label
role=frontendcan only perform the REST API callGET /userdata/[0-9]+, all other API interactions withrole=backendare restricted.- Proxy Injection : Envoy - Docs , Envoy
- Cilium is capable of transparently injecting a Layer 4 proxy into any network connection. This is used as the foundation to enforce higher level network policies (see DNS based and Layer 7 Examples).
- Proxy Injection : Envoy - Docs , Envoy

NETWORK POLICY 관련 eBPF Datapath

- Prefilter: An XDP program and provides a set of prefilter rules used to filter traffic from the network for best performance.
- Endpoint Policy: 정책에 따라 패킷을 차단/전달하거나, 서비스로 전달하거나, L7 로 정책 전달 할 수 있다.
- the Cilium datapath responsible for mapping packets to identities and enforcing L3 and L4 policies.
- L7 Policy: The L7 Policy object redirect proxy traffic to a Cilium userspace proxy instance. Cilium uses an Envoy instance as its userspace proxy. Envoy will then either forward the traffic or generate appropriate reject messages based on the configured L7 policy.
- → L7 정책는 커널 hookpoint 와 Userspace Proxy 사용으로 성능이 조금 떨어질 수 있다

Demo Application
# 배포
kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/1.16.3/examples/minikube/http-sw-app.yaml
kubectl get all
# 파드 라벨 확인
kubectl get pod --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE LABELS
deathstar-689f66b57d-4rwkf 1/1 Running 0 113s app.kubernetes.io/name=deathstar,class=deathstar,org=empire,pod-template-hash=689f66b57d
deathstar-689f66b57d-8p2l5 1/1 Running 0 113s app.kubernetes.io/name=deathstar,class=deathstar,org=empire,pod-template-hash=689f66b57d
tiefighter 1/1 Running 0 113s app.kubernetes.io/name=tiefighter,class=tiefighter,org=empire
xwing 1/1 Running 0 113s app.kubernetes.io/name=xwing,class=xwing,org=alliance
# cilium endpoint 확인
kubectl get ciliumendpoints
c1 endpoint list
c2 endpoint list
# 데스스타 SVC(ClusterIP) 접속하여 웹 파드 연결 확인 >> Hubble UI 에서 실시간 확인해보자!
kubectl exec xwing -- curl -s -XPOST deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/request-landing
Ship landed
kubectl exec tiefighter -- curl -s -XPOST deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/request-landing
Ship landed
# 확인
hubble observe

Identity-Aware and HTTP-Aware Policy Enforcement Apply an L3/L4 Policy - Link & Hubble CLI
- Cilium 에서는 Endpoint IP 대신, 파드의 Labels(라벨)을 사용(기준)하여 보안 정책을 적용합니다
- IP/Port 필터링을 L3/L4 네트워크 정책이라고 한다
- 아래 처럼 'org=empire' Labels(라벨) 부착된 파드만 허용해보자
- Cilium performs stateful connection tracking 이므로 리턴 트래픽은 자동으로 허용됨

# L3/L4 정책 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2"
kind: **CiliumNetworkPolicy**
metadata:
name: "rule1"
spec:
description: "L3-L4 policy to restrict deathstar access to empire ships only"
endpointSelector:
matchLabels:
org: empire
class: deathstar
ingress:
- fromEndpoints:
- matchLabels:
org: empire
toPorts:
- ports:
- port: "80"
protocol: TCP
EOF
# 정책 확인
kubectl get cnp
kc describe cnp rule1
c0 policy get
# 파드 curl 접속 시도 시 파드 sh 접속 후 curl 시도하자!
# 데스스타 SVC(ClusterIP) 접속하여 웹 파드 연결 확인 >> Hubble UI 에서 **drop** 확인!
kubectl exec tiefighter -- curl -s -XPOST deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/request-landing
Ship landed
kubectl exec xwing -- curl -s -XPOST deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/request-landing
**drop**
# hubble cli 모니터링
hubble observe --pod xwing
hubble observe --pod tiefighter
hubble observe --pod deathstar
Dec 2 05:36:24.490: default/xwing:55464 <> default/deathstar-c74d84667-t7msh:80 Policy denied DROPPED (TCP Flags: SYN)
Dec 2 05:36:24.490: default/xwing:55464 <> default/deathstar-c74d84667-t7msh:80 Policy denied DROPPED (TCP Flags: SYN)
**hubble observe --pod deathstar --verdict DROPPED**
Nov 30 15:23:47.721: default/xwing:60086 <> default/deathstar-c74d84667-ksnbd:80 Policy denied **DROPPED** (TCP Flags: SYN)
Nov 30 15:23:47.721: default/xwing:60086 <> default/deathstar-c74d84667-ksnbd:80 Policy denied **DROPPED** (TCP Flags: SYN)
Nov 30 15:27:40.250: default/tiefighter:41656 -> default/deathstar-c74d84667-ksnbd:80 http-request **DROPPED** (HTTP/1.1 PUT http://deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/exhaust-port)
Nov 30 15:28:00.707: default/tiefighter:41666 -> default/deathstar-c74d84667-ksnbd:80 http-request **DROPPED** (HTTP/1.1 PUT http://deathstar.default.svc.cluster.local/v1/exhaust-port)
**Inspecting the Policy**
# If we run cilium endpoint list again we will see that the pods with the label org=empire and class=deathstar
# now have ingress policy enforcement enabled as per the policy above.
# endpoint list 에서 정책 적용 확인
**c1 endpoint list | grep deathstar**
**c2 endpoint list**
ENDPOINT **POLICY (ingress)** POLICY (egress) IDENTITY LABELS (source:key[=value]) IPv6 IPv4 STATUS
**ENFORCEMENT** ENFORCEMENT
312 Disabled Disabled 18300 k8s:class=xwing 172.16.2.161 ready
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.namespace.labels.kubernetes.io/metadata.name=default
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.cluster=default
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.serviceaccount=default
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=default
k8s:org=alliance
1972 **Enabled** Disabled 21144 **k8s:class=deathstar** 172.16.2.66 ready
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.namespace.labels.kubernetes.io/metadata.name=default
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.cluster=default
k8s:io.cilium.k8s.policy.serviceaccount=default
k8s:io.kubernetes.pod.namespace=default
k8s:org=empirec2 endpoint list
8. BandWidth Manager
설정
# 인터페이스 tc qdisc 확인
tc qdisc show dev ens5
qdisc mq 0: root
qdisc fq_codel 0: parent :4 limit 10240p flows 1024 quantum 1514 target 5ms interval 100ms memory_limit 32Mb ecn drop_batch 64
qdisc fq_codel 0: parent :3 limit 10240p flows 1024 quantum 1514 target 5ms interval 100ms memory_limit 32Mb ecn drop_batch 64
qdisc fq_codel 0: parent :2 limit 10240p flows 1024 quantum 1514 target 5ms interval 100ms memory_limit 32Mb ecn drop_batch 64
qdisc fq_codel 0: parent :1 limit 10240p flows 1024 quantum 1514 target 5ms interval 100ms memory_limit 32Mb ecn drop_batch 64
# 설정
helm upgrade cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system --reuse-values --set bandwidthManager.enabled=true
# 적용 확인
cilium config view | grep bandwidth
enable-bandwidth-manager true
# egress bandwidth limitation 동작하는 인터페이스 확인
c0 status | grep BandwidthManager
BandwidthManager: EDT with BPF [CUBIC] [ens5]
# 인터페이스 tc qdisc 확인 : 설정 전후 옵션값들이 상당히 추가된다
tc qdisc
tc qdisc show dev ens5
qdisc mq 8002: root
qdisc fq 8005: parent 8002:2 limit 10000p flow_limit 100p buckets 32768 orphan_mask 1023 quantum 18030b initial_quantum 90150b low_rate_threshold 550Kbit refill_delay 40ms timer_slack 10us horizon 2s horizon_drop
qdisc fq 8003: parent 8002:4 limit 10000p flow_limit 100p buckets 32768 orphan_mask 1023 quantum 18030b initial_quantum 90150b low_rate_threshold 550Kbit refill_delay 40ms timer_slack 10us horizon 2s horizon_drop
qdisc fq 8004: parent 8002:3 limit 10000p flow_limit 100p buckets 32768 orphan_mask 1023 quantum 18030b initial_quantum 90150b low_rate_threshold 550Kbit refill_delay 40ms timer_slack 10us horizon 2s horizon_drop
qdisc fq 8006: parent 8002:1 limit 10000p flow_limit 100p buckets 32768 orphan_mask 1023 quantum 18030b initial_quantum 90150b low_rate_threshold 550Kbit refill_delay 40ms timer_slack 10us horizon 2s horizon_drop
예제 배포
# 테스트를 위한 트래픽 발생 서버/클라이언트 파드 생성
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
annotations:
# Limits egress bandwidth to 10Mbit/s.
kubernetes.io/egress-bandwidth: "10M"
labels:
# This pod will act as server.
app.kubernetes.io/name: netperf-server
name: **netperf-server**
spec:
containers:
- name: netperf
image: cilium/netperf
ports:
- containerPort: 12865
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
# This Pod will act as client.
name: netperf-client
spec:
affinity:
# Prevents the client from being scheduled to the
# same node as the server.
podAntiAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
- labelSelector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app.kubernetes.io/name
operator: In
values:
- netperf-server
topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
containers:
- name: **netperf**
args:
- sleep
- infinity
image: cilium/netperf
EOF# egress BW 제한 정보 확인
kubectl describe pod netperf-server | grep Annotations:
Annotations: kubernetes.io/egress-bandwidth: 10M
# egress BW 제한이 설정된 파드가 있는 cilium pod 에서 제한 정보 확인
c1 bpf bandwidth list
c2 bpf bandwidth list
IDENTITY EGRESS BANDWIDTH (BitsPerSec)
904 10M
c1 endpoint list
c2 endpoint list
ENDPOINT POLICY (ingress) POLICY (egress) IDENTITY LABELS (source:key[=value]) IPv6 IPv4 STATUS
ENFORCEMENT ENFORCEMENT
904 Disabled Disabled 21565 k8s:app.kubernetes.io/name=netperf-server 172.16.2.153 ready
# 트래픽 발생 >> Hubble UI 에서 확인
# egress traffic of the netperf-server Pod has been limited to 10Mbit per second.
NETPERF_SERVER_IP=$(kubectl get pod netperf-server -o jsonpath='{.status.podIP}')
kubectl exec netperf-client -- netperf -t TCP_MAERTS -H "${NETPERF_SERVER_IP}"
Recv Send Send
Socket Socket Message Elapsed
Size Size Size Time Throughput
bytes bytes bytes secs. 10^6bits/sec
131072 16384 16384 10.00 9.54 # 10Mbps 제한 확인!
# 5M 제한 설정 후 테스트
kubectl get pod netperf-server -o json | sed -e 's|10M|5M|g' | kubectl apply -f -
c1 bpf bandwidth list
c2 bpf bandwidth list
kubectl exec netperf-client -- netperf -t TCP_MAERTS -H "${NETPERF_SERVER_IP}"
Recv Send Send
Socket Socket Message Elapsed
Size Size Size Time Throughput
bytes bytes bytes secs. 10^6bits/sec
131072 16384 16384 10.09 4.56 # 4.5Mbps 제한 확인!
# 20M 제한 설정 후 테스트
kubectl get pod netperf-server -o json | sed -e 's|5M|20M|g' | kubectl apply -f -
kubectl exec netperf-client -- netperf -t TCP_MAERTS -H "${NETPERF_SERVER_IP}"
Recv Send Send
Socket Socket Message Elapsed
Size Size Size Time Throughput
bytes bytes bytes secs. 10^6bits/sec
131072 16384 16384 10.00 18.95 # 19Mbps 제한 확인!
tc qdisc show dev ens5
# 삭제
kubectl delete pod netperf-client netperf-server